Aids or equipment
Refers to any aids, equipment or other devices used by a person with one or more disabilities to assist them with performing tasks. Does not include help provided by another person or an organisation.
Cared-accommodation
Refers to accommodation within health establishments, such as hospitals, nursing homes, aged care hostels, cared components of retirement villages, psychiatric institutions, and other 'homes', such as group homes for people with disability. The accommodation must include all meals for its occupants and provide 24-hour access to assistance for personal and/or medical needs. To be included in this survey a person must have been a resident, or expected to be a resident, of the cared-accommodation establishment for three months or more.
Cognitive/emotional
This activity comprises the following tasks:
- making friendships, maintaining relationships, or interacting with others
- coping with feelings or emotions
- decision making or thinking through problems
- managing own behaviour
Communication
This activity comprises the following tasks:
- understanding family or friends
- being understood by family or friends
- understanding strangers
- being understood by strangers
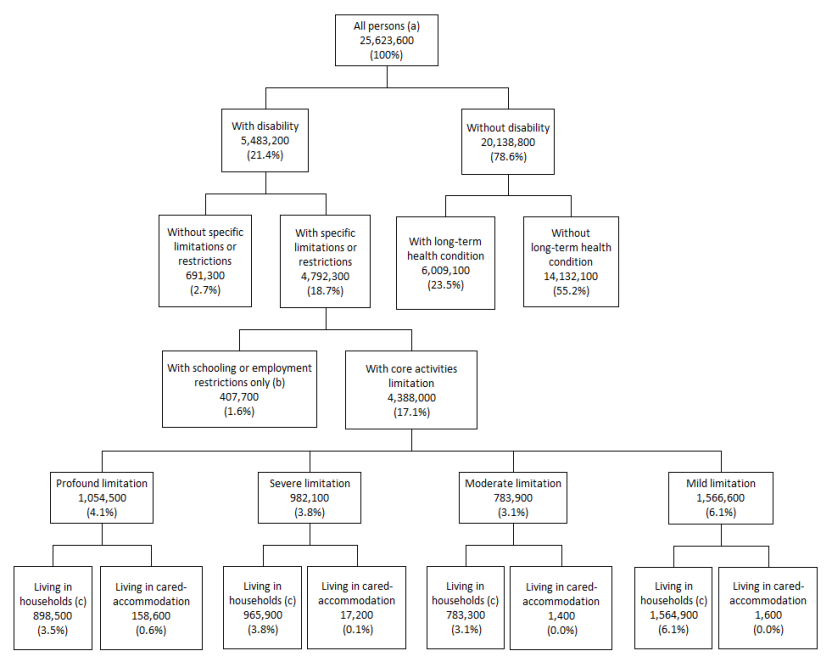
Core activities
Core activities are communication, mobility and self-care.
Core activity limitation
Four levels of core activity limitation are determined based on whether a person needs help, has difficulty, or uses aids or equipment with any of the core activities (mobility, self-care and communication). A person's overall level of core activity limitation is determined by their highest level of limitation in these activities.
The four levels of limitation are:
- profound - the person is unable to do, or always needs help with, a core activity task
- severe - the person:
- sometimes needs help with a core activity task, and/or
- has difficulty understanding or being understood by family or friends, or
- can communicate more easily using sign language or other non-spoken forms of communication
- moderate - the person needs no help, but has difficulty with a core activity task
- mild - the person needs no help and has no difficulty with any of the core activity tasks, but:
- uses aids or equipment for core tasks, or has one or more of the following limitations
- cannot easily walk 200 metres
- cannot walk up and down stairs without a handrail
- cannot easily bend to pick up an object from the floor
- needs assistance or has difficulty using public transport or cannot use it at all
Disability type
The International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) defines disability as an umbrella term for impairments, activity limitations and participation restrictions.
In this survey, a person has a disability if they report they have a limitation, restriction or impairment, which has lasted, or is likely to last, for at least six months and restricts everyday activities. This includes:
- loss of sight (not corrected by glasses or contact lenses)
- loss of hearing where communication is restricted, or an aid to assist with, or substitute for, hearing is used
- speech difficulties
- shortness of breath or breathing difficulties causing restriction
- chronic or recurrent pain or discomfort causing restriction
- blackouts, seizures, or loss of consciousness
- difficulty learning or understanding
- incomplete use of arms or fingers
- difficulty gripping or holding things
- incomplete use of feet or legs
- nervous or emotional condition causing restriction
- restriction in physical activities or in doing physical work
- disfigurement or deformity causing restriction
- mental illness or condition requiring help or supervision
- memory problems or periods of confusion causing restriction
- social or behavioural difficulties causing restriction
- long-term effects of head injury, stroke or other acquired brain injury causing restriction
- receiving treatment or medication for any other long-term conditions or ailments and still being restricted
- any other long-term conditions resulting in a restriction
Episodic care
Refers to care that is only provided during episodes where the condition of the main/only recipient deteriorates. That is, for conditions where the main/only recipient experiences attacks or relapses at intervals (e.g. episodes of schizophrenia, epilepsy, etc.).
Formal assistance/providers
Help provided to persons with disability or persons aged 65 years or over by:
- organisations or individuals representing organisations (whether profit making or non-profit making, government or private); or
- other persons (excluding family, friends or neighbours as described in Informal assistance/providers), on a regular, paid basis, who are not associated with any organisation.
Health care
This activity comprises:
- foot care
- taking medication or administering injections
- dressing wounds
- using medical equipment
- manipulating/exercising muscles or limbs
- skin care
- prevention of pressure sores
- therapeutic massage
Impairment
In the context of health experience, an impairment is defined by the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) as a loss or abnormality in body structure or physiological function (including mental functions). Abnormality is used to refer to a significant variation from established statistical norms.
Examples of an impairment are loss of sight or loss of a limb, disfigurement or deformity, impairment of mood or emotion, impairments of speech, hallucinations, loss of consciousness, or any lack of function of body organs.
Informal assistance/providers
Unpaid help or supervision that is provided to persons with disability or persons aged 65 years and over. It only includes assistance that is provided because of a person's disability or because they are older. Informal assistance may be provided by family, friends or neighbours regardless of whether they received Carer Payment or other allowances.
Level of communication limitation
Four levels of communication limitation are determined based on whether a person needs help, has difficulty, or uses aids or equipment in communicating with others. A person's overall level of communication limitation is determined by their highest level of limitation in these activities.
The four levels of limitation are:
- profound - the person cannot understand or be understood at all. They always need help when communicating with family or friends and people they don't know.
- severe - the person:
- communicates more easily with sign language or other non-spoken communication
- sometimes needs help understanding or being understood by someone they don't know
- sometimes needs help understanding or being understood by family or friends
- doesn't need help, but has difficulty understanding or being understood by family or friends.
- moderate - the person doesn't need help, but has difficulty understanding or being understood by someone they don't know
- mild - the person has no difficulty understanding or being understood by someone else, but uses a communication aid
Level of employment restriction
Four levels of employment restriction are determined based on whether a person needs help, has difficulty, or uses aids or equipment in their employment. A person's overall level of employment restriction is determined by their highest level of limitation in these activities.
The four levels of restriction are:
- profound - the person's condition permanently prevents them from working
- severe - the person:
- requires personal support
- needs ongoing supervision or assistance
- requires a special disability support person
- receives assistance from a disability job placement program or agency
- moderate - the person is restricted in the type of job and/or the numbers of hours they can work or has difficulty in changing jobs
- mild - the person needs:
- special equipment or additional software
- modifications to buildings or fittings
- special arrangements for transport or parking
- training
- to be allocated different duties
Level of mobility limitation
Four levels of mobility limitation are determined based on whether a person needs help, has difficulty, or uses aids or equipment in moving around. A person's overall level of mobility limitation is determined by their highest level of limitation in these activities.
The four levels of limitation are:
- profound - the person:
- does not get out of bed
- does not move around the residence
- does not leave home because of their condition
- always needs help or supervision with:
- moving around places away from their place of residence
- moving about their place of residence
- getting into or out of a bed or chair
- severe - the person sometimes needs help or supervision with:
- moving around places away from their place of residence
- moving about their place of residence
- getting into or out of a bed or chair
- moderate - the person has difficulty, but doesn't need help with:
- moving around places away from their place of residence
- moving about their place of residence
- getting into or out of a bed or chair
- mild - the person doesn't need any help and doesn't have any difficulty with moving around, but:
- uses a mobility aid
- cannot easily walk 200 metres or takes longer to do so than most people their age
- cannot walk up or down stairs without using a handrail
- cannot easily bend to pick something off the floor
- cannot use public transport
- can use public transport, but needs help or supervision
- needs no help or supervision, but has difficulty using public transport
Level of non-school educational restriction
Three levels of non-school educational restrictions are determined based on whether a person needs help, has difficulty, or uses aids or equipment in their education. A person's overall level of non-school educational restriction is determined by their highest level of limitation in these activities.
The three levels of restriction are:
- severe - the person:
- receives special tuition
- receives assistance from a counsellor/disability support person
- moderate - the person:
- often needs time off from school/institution
- has difficulty at school/institution because of their condition(s)
- has special assessment procedures
- mild - the person needs:
- special equipment
- special transport arrangements
- special access arrangements
- other special arrangements or support services
Level of schooling restriction
Four levels of schooling restrictions are determined based on whether a person needs help, has difficulty, or uses aids or equipment in their education. A person's overall level of schooling restriction is determined by their highest level of limitation in these activities.
The four levels of restriction are:
- profound - the person's condition prevents them from attending school
- severe - the person:
- attends a special school or special classes
- receives special tuition
- receives assistance from a counsellor/disability support person
- moderate - the person:
- often needs time off from school
- has difficulty at school because of their condition(s)
- has special assessment procedures
- mild - the person needs:
- special equipment
- special transport arrangements
- special access arrangements
- other special arrangements or support services
Level of self-care limitation
Four levels of self-care limitation are determined based on whether a person needs help, has difficulty, or uses aids or equipment in looking after themselves. A person's overall level of self-care limitation is determined by their highest level of limitation in these activities.
The four levels of limitation are:
- profound - the person always needs help or supervision with:
- bathing or showering
- dressing
- eating
- toileting
- managing bladder or bowel control
- severe - the person sometimes needs help or supervision with:
- bathing or showering
- dressing
- eating
- toileting
- managing bladder or bowel control
- moderate - the person has difficulty, but doesn't need help with:
- bathing or showering
- dressing
- eating
- toileting
- managing bladder or bowel control
- mild - the person:
- doesn't need any help and doesn't have any difficulty with self-care, but uses an aid
- does not use the toilet, but does not have difficulty controlling their bladder or bowel
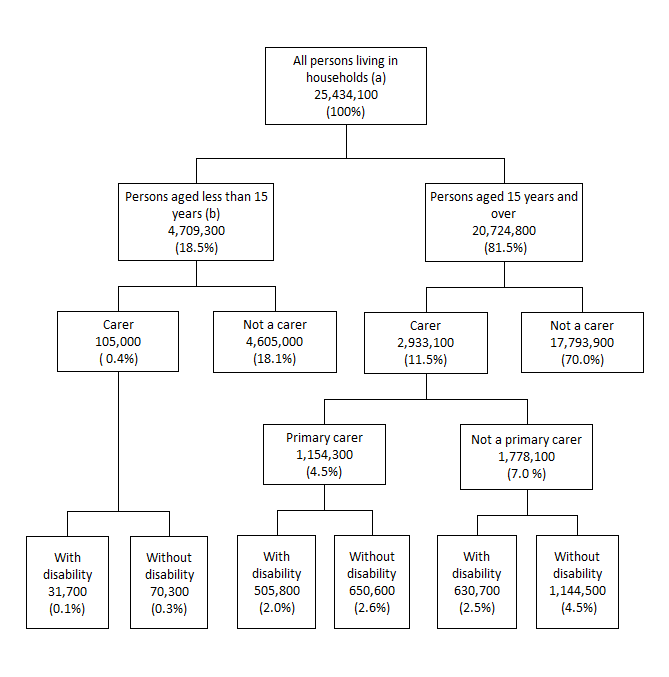
Living in households
A person is included in the 'Living in households' population if they are part of a household and reside in a private dwelling or self-care retirement village. A person living in cared-accommodation is excluded from the 'Living in households' population.
Long-term health condition
A disease or disorder that has lasted, or is likely to last, for six months or more and is current at the time of the survey. Conditions were classified based on the International Classification of Diseases: 10th Revision (ICD).
Main recipient of care
Where a primary carer is caring for more than one person, the main recipient of care is the one receiving the most help or supervision. A sole recipient is also classed as a main recipient. The assistance has to be ongoing, or likely to be ongoing, for at least six months and be provided for one or more of the core activities of communication, mobility and self-care.
Mobility
This activity comprises the following tasks:
- getting into or out of a bed or chair
- moving about the usual place of residence
- going to or getting around a place away from the usual residence
- walking 200 metres
- walking up and down stairs without a handrail
- bending and picking up an object from the floor
- using public transport
Need for assistance
A person with one or more disabilities, or aged 65 years and over, is identified as having a need for assistance with an activity if, because of their disability or age, they report that they need help or supervision with at least one of the specified tasks constituting that activity. Need is not identified if the help or supervision is required because the person has not learned, or has not been accustomed to performing that activity. The person is considered to need assistance whether or not assistance is actually received.
Non-core activities
These include cognitive or emotional tasks, health care, meal preparation, reading or writing, household chores, property maintenance and transport.
Other carer
See Carers.
Primary carer
See Carers.
Property maintenance
This activity includes light maintenance and gardening tasks, such as:
- changing light bulbs, tap washers
- making minor home repairs
- mowing lawns, watering, pruning shrubs, weeding, planting, turning soil
- removing rubbish
Reading or writing
This activity includes tasks such as:
- checking bills or bank statements
- writing letters
- filling in forms
Secondary carer
See Carers.
Self-care
This activity comprises the following tasks:
- showering or bathing
- dressing
- eating
- toileting
- bladder or bowel control