| ABARES | Australia Bureau of Agricultural and Resource Economics and Sciences (division of Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry (DAFF)) |
| ABS Agricultural Survey | A collective term used to refer to the Rural Environment and Agricultural Commodities Survey (REACS), Agricultural Census, Agricultural Resource Management Survey and annual pre-2008 Agricultural Surveys |
| Adult female cattle | Cows and heifers 1 year and over |
| Adult male cattle | All other beef cattle not elsewhere classified (e.g. steers and bulls) |
| Breeding cows | Adult female cattle that are mated/joined to a bull, synonymous with Mated cows |
| Calves | Calves that are born alive, are branded and are less than 1 year old |
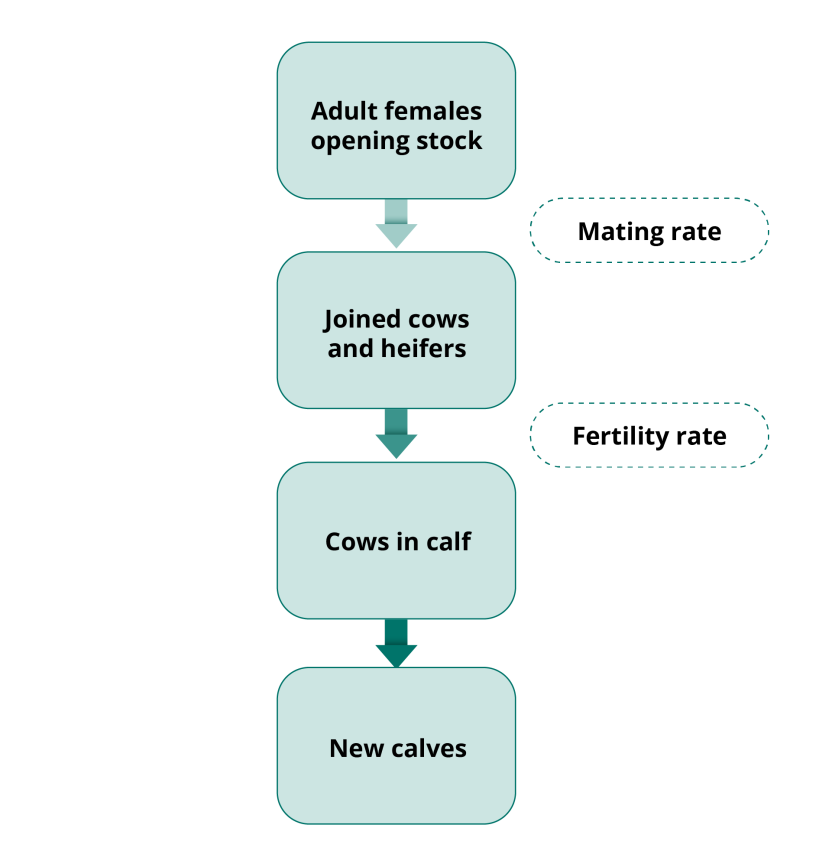
| Calving rate | Number of calves surviving birth, as a percentage of the number of mated females from the previous year |
| Dairy cattle | Cattle bred to produce large quantities of milk. Dairy producers raise dairy calves to replace dairy cows that are removed from the herd for various reasons (e.g. low milk production). Bobby calves are calves that are surplus to the dairy industry requirements as they are not suitable for the dairy herd. These include all bull calves (males) and 1/4 of females calves born each year. On average, at least 400,000 bobby calves are sent to slaughter. |
| Estimated Value of Agricultural Operations (EVAO) | An ABS construct used to estimate the relative size of agricultural activity undertaken by a business. Data scope include establishments with EVAO of $5,000 or more from 1993-94 to 2014-15 and EVAO of $40,000 or more from 2015-16 to 2021-22. |
| Export | Number of live cattle sold to other countries |
| Farm-gate | Net value of agricultural product produced on farm, which excludes marketing, transport, or other downstream costs |
| Fertility rate | The percentage of cows that, having been mated with a bull, will successfully give birth to calves that survive until they are marked |
| Herd size | Total number of beef cattle. Sum of calves, adult female cattle and adult male cattle |
| Herd structure/composition | Ratio of number of calves to number of adult female cattle to number of adult male cattle |
| Historical herd | Number of total beef cattle in the previous Agricultural Surveys |
| Livestock on holding | Number of cattle on holding at 30 June |
| Livestock slaughter/disposal | Livestock slaughtered at registered commercial abattoirs and meat processors for meat production for human consumption |
| Marked Calves | Calves that have been tagged/tattooed and are officially in the farm’s administrative data |
| Marking | The process whereby calves receive an ear tattoo or tag, and male calves are castrated |
| Mated cows | Adult female cattle that are mated/joined to a bull, synonymous with breeding cows |
| Mating rate | Percentage of adult female cattle that are mated/joined with bull |
| Meat cattle | Cattle raised for meat production. Synonym for beef cattle |
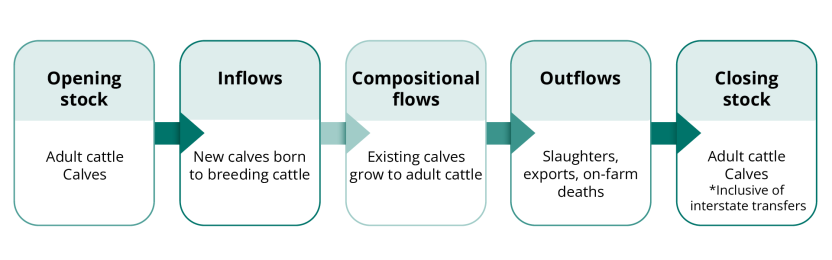
| Model closing stock | Number of cattle remaining on holding on 30th June |
| Model inflow | Includes production of new calves |
| Model opening stock | Initial number of cattle at the start of the reference year |
| Model outflow | Includes cattle slaughter and exports |
| Mortality rate | On farm deaths where beef cattle die before slaughter |
| Non-breeding cows | Adult female cattle that are not mated/joined to a bull |
| Slaughter weight | Weight at which cattle are sent to the abattoir for processing |
| Slaughter yard/abattoir | Place where cattle are slaughtered for beef production |
| Subpopulation | Catch-all term for male, female and calf populations as individual populations, as opposed to totals. |
| Turn-off rate | Rate at which cattle are sold or removed from property (farm or feedlot) for beef processing or export |