There are upcoming changes to the Innovation in Australian Business release.
See ‘Survey impacts and changes’ for more information.
Statistics in this release present key innovation data for Australian businesses, as collected from the 2022-23 Business Characteristics Survey (BCS).
There are upcoming changes to the Innovation in Australian Business release.
See ‘Survey impacts and changes’ for more information.
Innovation in Australian Business 2022-23 is the second release of the redeveloped innovation module.
This release will be the first with directly comparable data for the redeveloped survey.
Customised data requests are also available on request. Please see Contact Us page.
An innovation-active business is one that introduced any type of innovation (i.e., new good, service or process), and/or had innovation which was still in development (as of 30 June 2023) or abandoned during the reference period (i.e., the two years ended 30 June 2023).
An innovating business is one that introduced any type of innovation (i.e., any new good, service and/or process) during the reference period (i.e., the two years ended 30 June 2023).
| Businesses with innovative activity which was: | 0-4 persons | 5-19 persons | 20-199 persons | 200 or more persons | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| introduced (innovating businesses) | 34 | 46 | 57 | 57 | 39 |
| still in development(b) | 19 | 29 | 39 | 45 | 23 |
| abandoned | 9 | 13 | 16 | 13 | 11 |
| any innovative activity (innovation-active businesses) | 40 | 54 | 65 | 63 | 46 |
For the two years ended 30 June 2023, estimates for the core innovation indicators (i.e., innovation-active, and innovating businesses) were 46% and 39% respectively, compared to 52% and 45% for the two years ended 30 June 2021.
| Types of innovation | 0-4 persons | 5-19 persons | 20-199 persons | 200 or more persons | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goods or services | 20 | 23 | 34 | 26 | 22 |
| Process | 25 | 39 | 48 | 53 | 31 |
For the two-year reference period ended 30 June 2023:
The image represents a map of Australia showing the individual states and territories, highlighted in different colours.
The proportion of innovation-active businesses for the two years ended 30 June 2023 are displayed in the image within the boundary of the state or territory with the exception of the Australian Capital Territory and Tasmania which have the proportions positioned external to the map boundary, with an arrow linking it to the relevant boundary on the map.
The proportion of innovation-active businesses for the two years ended 30 June 2023 for each state and territory are 45% for New South Wales, 47% for Victoria, 47% for Queensland, 45% for South Australia, 42% for Western Australia, 39% for Tasmania, 48% for the Northern Territory and 46% for the Australian Capital Territory.
For the first time, businesses that reported innovation activity were asked whether any environmental benefits were obtained as a result of innovation activity.
For the two years ended 30 June 2023:
For the two years ended 30 June 2023, 42% of businesses reported barriers to innovation, down from 46% reported in the two years ended 30 June 2021.
Businesses that reported innovation activity were asked if they collaborated with others to develop or introduce new goods, services or processes in the two years ended 30 June 2023.
Innovation-active businesses were also asked whether they entered into any fee-for-service arrangements to develop or introduce new goods, services, or processes.
A third of innovation-active businesses (33%) either collaborated and/or entered into a fee-for-service arrangement for the purpose of innovation, compared to 36% in the two years ended 30 June 2021.
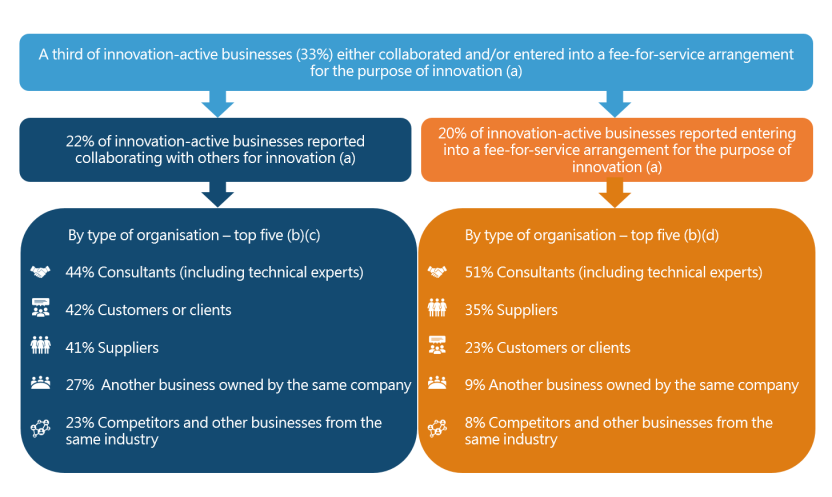
The image contains five rectangular boxes. The box at the top, shaded in light blue, presents the following information: A third of innovation-active businesses (33%) either collaborated and/or entered into a fee-for-service arrangement for the purpose of innovation.
There are two arrows underneath pointing to the two boxes positioned under the top box. The box on the left side, shaded in dark blue illustrates the proportion of innovation-active businesses that reported collaboration for the purpose of innovation during the two years ended 30 June 2023 (22%). The box on the right side, shaded in orange, illustrates the proportion of innovation-active businesses that reported entering into a fee-for-service arrangement for the purpose of innovation during the two years ended 30 June 2023 (20%). There is an arrow underneath each of the rectangular boxes pointing down to larger boxes with rounded edges that present the top five types of organisations that businesses collaborated with or had a fee-for-service arrangement with. The arrows and larger boxes are the same colour as those above (dark blue on the left side and orange on the right side).
The top five types of organisations that innovation-active businesses reported collaborating with were: "Consultants (including technical experts)” (44%), "Customers or clients" (42%), "Suppliers" (41%), "Another business owned by the same company" (27%), and "Competitors and other businesses from the same industry" (23%).
The top five types of organisations that innovation-active businesses reported entering into a fee-for-service arrangement with were: "Consultants (including technical experts)” (51%), "Suppliers" (35%), "Customers or clients" (23%), "Another business owned by the same company" (9%), and "Competitors and other businesses from the same industry" (8%).
In the two years ended 30 June 2023, 48% of innovation-active businesses reported factors that prevented or limited collaboration for innovation, compared to 50% reported in the two years ended 30 June 2021.
Businesses that reported innovation activity were asked to estimate the expenditure (using ranges) on the development or introduction of new or significantly improved goods and/or services or processes during the year ended 30 June 2023.
Business expenditure on innovation activities may include expenditure on labour costs, training, external services, materials, Research and Experimental Development (R&D), capital goods, etc. related to the new or significantly improved goods and/or services or processes.
Of innovation-active businesses:
| 0-4 persons | 5-19 persons | 20-199 persons | 200 or more persons | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No expenditure | 32 | 27 | 24 | 13 | 30 |
| $1 to less than $25,000 | 49 | 42 | 28 | 12 | 44 |
| $25,000 to less than $50,000 | 9 | 15 | 12 | 7 | 11 |
| $50,000 to less than $100,000 | 6 | 7 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
| $100,000 to less than $250,000 | 3 | 4 | 9 | 15 | 4 |
| $250,000 to less than $1,000,000 | 1 | 3 | 9 | 22 | 3 |
| $1,000,000 to less than $5,000,000 | np | np | 6 | 15 | 1 |
| $5,000,000 or more | np | np | 1 | 7 | - |
np not available for publication but included in totals where applicable, unless otherwise indicated.
- nil or rounded to zero (including null cells).
Innovation-active businesses that reported innovation expenditure were also asked to provide a percentage breakdown of their innovation related expenditure against a list of activities related to innovation.
Where a business reported any percentage, they were deemed to have undertaken that activity.
| Innovation-active businesses | |
|---|---|
| Acquisition of machinery, equipment or technology to develop or introduce new or significantly improved goods, services or processes | 41 |
| Marketing activities undertaken to introduce new or significantly improved goods and/or services | 37 |
| Training relevant to the development or introduction of new or significantly improved goods, services or processes | 37 |
| Other labour costs related to the development or introduction of new or significantly improved goods, services or processes not included in other categories | 35 |
| Re-organisation of existing business models, work practices and decision making processes | 31 |
| Design, planning or testing to develop or introduce new or significantly improved goods, services or processes | 31 |
| Research and Experimental Development performed by this business | 31 |
| Acquisition of licenses, rights, patents or other intellectual property | 17 |
| Research and Experimental Development acquired from other businesses or institutions | 11 |
| Other activities related to the development or introduction of new or significantly improved goods, services or processes | 6 |
For the year ended 30 June 2023, innovating businesses were asked to estimate the percentage of income that resulted from the sale of new or significantly improved goods and/or services.
Innovating businesses were also asked to estimate the percentage of cost savings that resulted from the introduction of new or significantly improved processes.
Innovating businesses were asked to provide details about their most significant innovation introduced during the two years ended 30 June 2023.

The image contains four rectangular boxes representing the most significant innovation introduced, as reported by innovating businesses, by target market(s) of the business’s most significant innovation, and top three commercialisation activities undertaken for the business’s most significant innovation, in the two years ended 30 June 2023.
The image has two rectangular boxes at the top which show the proportion of innovating businesses whose most significant innovation was a new good or service (on the left side) or a new business process (on the right side) during the two years ended 30 June 2023. The boxes are shaded in light blue and dark blue, respectively. A new "good or service" was reported as the most significant innovation by 47% of innovating businesses and a new "business process" was reported as the most significant innovation by 53% of innovating businesses.
There are two arrows underneath pointing to the box positioned under the top boxes. The large, orange, rectangular box with rounded edges, below the two rectangular boxes at the top represents the five target markets for an innovating business's most significant innovation and the proportion of innovating businesses that targeted these markets during the two years ended 30 June 2023. The proportions reported for each target market were: "Customers: Within the same state/territory" (56%), "Internal business product or process (i.e., no target market outside of business)” (28%), "Customers: Outside the state/territory but within Australia" (22%), "Customers: Rest of the world" (i.e., Europe, Americas, Africa) (7%) and "Customers: Oceania/Asia" (7%).
There is one arrow underneath the orange box in the middle, pointing to the bottom box. The large, red, rectangular box with rounded edges represents the top three commercialisation activities undertaken for an innovating business's most significant innovation, and the proportion of innovating businesses that undertook the activities during the two years ended 30 June 2023. The top three activities were: "Market research" (26%), "Training on how to market the good, service or process" (13%), and "Acquisition of licenses, rights, patents and/or other intellectual property” (8%).
Caution: Data in Data Explorer is currently released after the 11:30am release on the ABS website. Please check the reference period when using Data Explorer.
For information on Data Explorer and how it works, see the Data Explorer user guide.
Business information and performance, year ended 30 June 2023
This release previously used catalogue number 8158.0
The ABS reviews and makes changes to its Forward Work Program to ensure it continues to appropriately measure the Australian economy, environment and society. The increasing appreciation of the value of data is generating significant additional demand for services of the ABS. As the growth in opportunities exceeds the capacity of the ABS, statistical outputs are prioritised. As a result of prioritisation, there will be changes to the Innovation in Australian Business release.
From 2024-25 the Business Characteristics Survey will move to a biennial frequency, that is, collecting and publishing data every second year, rather than every year.
Given the change in frequency, the ABS is currently reviewing what data will be collected in the survey, as well as publication content, to ensure we can continue to provide high quality business characteristics data that is important to users, on the new biennial frequency.
The ABS invites feedback through the ABS Consultation Hub, and will make decisions on changes to the collection based on the information gathered in this consultation.