 CHARACTERISTICS OF PARTICIPATION
CHARACTERISTICS OF PARTICIPATION
TYPE OF PARTICIPATION
People can choose to take part in sport and physical recreation either through organised or non-organised activities. Organised activities can be arranged through recreation clubs, sporting or non-sporting associations, through gymnasiums or through a wide variety of other sporting and non-sporting arrangements. Around a quarter of the population (27%) reported participating in organised sport and physical recreation while almost double that (53%) took part in non-organised activity (Table 3).
Participation in organised sport and physical recreation was highest amongst persons aged 15–17 years (58%). Participation rates in organised activities were similar for males and females (28% and 27% respectively) but were higher for males (54%) than females (51%) in non-organised activities (Table 3).
FREQUENCY OF PARTICIPATION
Of the 11.7 million people who participated in sport and physical recreation in the 12 months prior to interview, more than half (52%) participated 105 times or more (i.e. on average at least two times each week). This included the number of times spent training and practising for an activity. A larger percentage of female than male participants took part 105 times or more (55% compared with 49% respectively) (Table 4).
Comparing the top 25 most frequently participated in sports and physical activities, persons walking for exercise were more likely to participate 105 times or more (58%). This was followed by fitness and gym activities, where 40% of participants participated 105 times or more (Tables 8).
FACILITIES USED
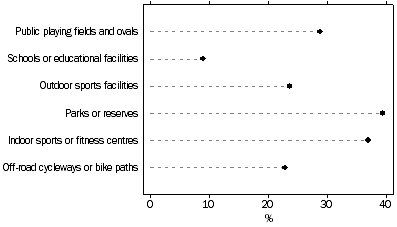
There is a wide range of facilities available to people who participate in sport and physical recreation. Not all are purpose built such as ovals, tennis courts and gymnasiums with parks, beaches and walking trails also often used for exercise and physical activity. Those who participated in sport and physical recreation were asked whether they had used any of six selected facilities in the 12 months before interview (see graph below). Parks and reserves were used by the most people (40%), followed by indoor sports and fitness centres (37%).
Participants, Sport and physical recreation, By selected facilities
POPULAR SPORTS AND ACTIVITIES
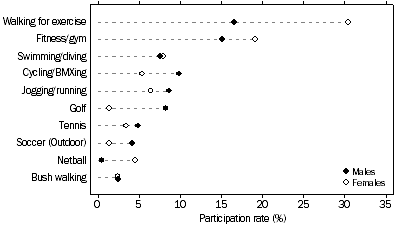
Walking for exercise was the most popular physical recreational activity, with 24% of the population walking for exercise at least once in the 12 months prior to interview. Females were almost twice as likely to walk for exercise than males (30% and 17% respectively). Participation rates for walking for exercise were highest for persons aged 55–64 years (36%), and lowest for persons aged 15–17 years (6.3%).
The next most popular activity group was fitness or gym activities (17%). More females than males participated in fitness or gym activities (19% and 15% respectively). Fitness or gym activities were most popular for those aged 18–24 years (29%). (Tables 6 and 7)
Participation in most popular sports and physical recreation activities, By sex
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All
 Quality Declaration
Quality Declaration