INTERNATIONAL COMPARISON
Life expectancy
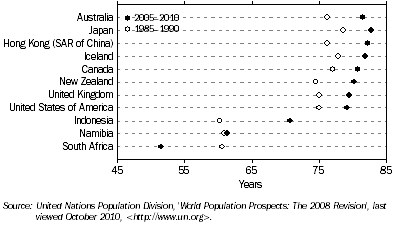
Australians have a life expectancy at birth which compares well with that experienced in other developed nations. According to the United Nations in World Population Prospects: The 2008 Revision (2009), global life expectancy at birth for 2005-2010 (medium variant) is estimated to be 65.4 years for males and 69.8 years for females. ABS life tables for 2007-2009 indicate that life expectancy at birth for Australian males (79.3 years) and females (83.9 years) continue to be among the highest in the world.
According to United Nations estimates for 2005-2010, life expectancy at birth of Australian males is exceeded only by Iceland, Hong Kong (SAR of China) and Switzerland. Life expectancy at birth of Australian females is exceeded by Japan, Hong Kong (SAR of China), France, Switzerland, and Spain.
Combined Australian male and female life expectancy at birth for 2005-2010 was 81.5 years. This was higher than the level for Canada (80.7 years), New Zealand (80.2 years), the United Kingdom (79.4 years) and the United States of America (79.2 years).
2.12 Life Expectancy at Birth, Selected countries
Infant mortality rate
In
World Population Prospects: The 2008 Revision (2009), the United Nations estimates the global infant mortality rate for 2005-2010 to be 47.3 infant deaths per 1,000 live births. The United Nations estimate of Australia's IMR (4.5 infant deaths per 1,000 live births) is among the lowest in the world, lower than that of New Zealand (4.6), Canada and the United Kingdom (both 4.8), and the United States of America (5.9). Iceland (2.9) has the lowest IMR, followed by Singapore (3.0) and Sweden (3.1).
On a regional basis, Northern America has the lowest IMR, with 5.8 infant deaths per 1,000 live births, followed by Europe (7.2). The world's regions recording the highest IMRs are Africa (82.6), followed by Asia (41.5), Oceania (22.8), which includes Australia, and then Latin America and the Caribbean (21.8).
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All