VITAL STATISTICS
Introduction
Births
Fertility rates
Deaths
Life expectancy
Causes of death
Introduction
The statistics presented in this commentary are the latest available at the time of publishing and will be updated or added to on a continuing basis.
Vital statistics relate to specified and defined vital events such as births, deaths, marriages and divorces, the relevant characteristics of the events themselves and of the person or persons concerned. This commentary focuses on a subset of these events, that is births and deaths in the Australian Capital Territory (ACT).
Vital statistics are an essential input for the planning of human development. Knowledge of the size and characteristics of a country’s population on a timely basis is a prerequisite to socioeconomic planning. Because a population increases by the addition of births and decreases by the subtraction of deaths, information about the number of births and deaths occurring in a population is crucial for estimating the natural increase (or decrease) and the annual change in population size and structure for that population. Information on the number of births occurring over a time period, classified by various characteristics of the women giving birth, constitutes the basis for analysis of the dynamics of reproduction. Information on deaths, classified by various characteristics of the deceased, especially age and sex, is necessary for calculating life-tables and estimating the probability of dying at various ages. The fertility and mortality estimates, derived from births and deaths statistics respectively, are essential for a variety of purposes, including an understanding of the growth dynamics of the population concerned; an assessment of the human aspects of socioeconomic development; the measurement of the risks of dying for males and females at specific ages for insurance and social security purposes; and for population projections. (Endnote 1)
Statistics on births and deaths in the ACT are compiled by the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) from information provided by the ACT Office of Regulatory Services. Refer to Births, Australia (cat. no. 3301.0) and Deaths, Australia (cat. no. 3302.0) for details. The statistics are compiled for a calendar year in which the birth or death was registered. Birth statistics are presented on the basis of place of usual residence of the mother and death statistics are presented on the basis of place of usual residence of the deceased.
Births
In 2008, there were 4,800 births registered to mothers usually resident in ACT. Of these, 4,700 births occurred within the ACT while an additional 90 births occurred interstate. The total of 4,800 births to ACT mothers is an increase of 1% on the previous year. The sex ratio at birth was 106 male births to every 100 female births and this was only marginally above the national average. Of the 4,800 births 170 were multiple births, of which, all were twins (i.e. 86 confinements).
Due to cross-border mobility as a result of the geographic proximity of the ACT and NSW, typically there are more births registered in the ACT each year than there are births to mothers usually resident in the ACT. In 2008, there were 5,600 births registered in the ACT. Of these 4,700 (84%) were to ACT mothers while 900 (16%) lived outside the ACT. By far the majority of these non-ACT births were to mothers who lived in NSW.
It should be noted that births usually have a time interval (or lag) between occurrence and registration, which can be attributed to either a delay by the parent(s) in the submission of a form to the registry or a delay in registry processing. Of the 5,600 births registered in the ACT in 2008, 91% occurred in 2008, 8% occurred in 2007 and the remaining 1% occurred in 2006 or earlier years.
BIRTHS, Summary statistics: Australian Capital Territory |
|
 |  |  | 1998 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 |
|
| Births to mothers usually resident in the ACT |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 | Registered in the ACT | no. | 3 887 | 4 128 | 4 400 | 4 663 | 4 718 |
 | Registered elsewhere in Australia | no. | 95 | 78 | 79 | 90 | 86 |
 | Total | no. | 3 982 | 4 206 | 4 479 | 4 753 | 4 804 |
| Sex ratio at births(a) | rate | 101.5 | 102.3 | 105.5 | 104.4 | 105.7 |
| Births registered in the ACT |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 | To mothers usually resident in the ACT | no. | 3 887 | 4 128 | 4 400 | 4 663 | 4 718 |
 | To mothers resident elsewhere in Australia | no. | 596 | 817 | 885 | 936 | 930 |
 | Total | no. | 4 483 | 4 945 | 5 285 | 5 599 | 5 648 |
|
| (a) Number of male live births per 100 female live births. |
| Source: Births, Australia (cat. no. 3301.0), ABS data available on request, Births collection. |
Fertility rates
Total fertility rate is defined as the sum of age-specific fertility rates. It represents the number of children a woman would bear during her lifetime if at each year of her reproductive life she experienced the age-specific fertility rates of the current year. For additional reference, refer to the Glossary of Births, Australia (cat. no. 3301.0.
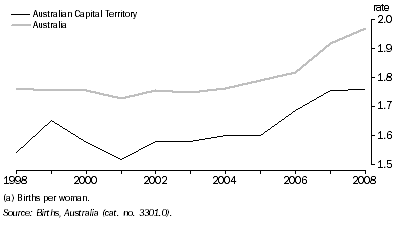
Over the last decade the total fertility rate for the ACT was consistently lower than the national average (see graph below).
Consistent with national trends, the age-specific fertility rates for 2008 in the ACT were highest for women aged 30-34 years (130.6 births per 1,000 women in this age group). While the ACT's total fertility rate for women has gradually increased from a low in 2001 of 1.52 to 1.76 in 2008 it is still much lower than the replacement level of 2.1 and it has the lowest teenage fertility rate in Australia.
The crude birth rate is the number of births registered during the calendar year per 1,000 estimated resident population at 30 June of that year. The crude birth rate for the ACT has risen from a low in 2005 of 12.7 to 13.9 births per 1,000 population recorded in both 2007 and 2008.
TOTAL FERTILITY RATE(a)
FERTILITY RATES, Australian Capital Territory |
|
 |  | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 |
 |  | rate | rate | rate | rate |
|
| Age-specific fertility rates(a) |  |  |  |  |
 | 15-19 years(b) | 9.1 | 9.1 | 10.3 | 8.0 |
 | 20-24 years | 31.8 | 32.5 | 34.5 | 35.3 |
 | 25-29 years | 82.2 | 87.7 | 92.3 | 84.3 |
 | 30-34 years | 118.3 | 125.2 | 127.8 | 130.6 |
 | 35-39 years | 66.4 | 69.3 | 71.5 | 77.5 |
 | 40-44 years | 12.0 | 13.5 | 13.8 | 15.5 |
 | 45-49 years(c) | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.5 |
| Total fertility rate(d) | 1.600 | 1.688 | 1.755 | 1.760 |
| Crude birth rate(e) | 12.7 | 13.4 | 13.9 | 13.9 |
|
| (a) Births per 1,000 women. |
| (b) Includes births to mother aged less than 15 years. |
| (c) Includes births to mother aged 50 years and over. |
| (d) Births per woman. |
| (e) Births per 1,000 estimated resident population. |
| Source: Births, Australia (cat. no. 3301.0). |
Deaths
For the most part, statistics presented in
Deaths, Australia (cat. no. 3302.0) refer to deaths registered during the calendar year. As with births, deaths are presented on the basis of state of usual residence of the deceased (unless otherwise stated), which may not necessarily be the state of occurrence or the state of registration of the death.
The total number of deaths of residents of the ACT increased in the past decade from 1,300 in 1998 to 1,700 deaths in 2008.
In 2008, a total of 1,900 deaths were registered in the ACT, of these 1,600 or 84% were usual residents of the ACT and the remainder were deaths of residents of other states.
Taking into account the effect of changes in the age structure of the ACT over time, the standardised death rate for the ACT decreased from 6.6 deaths to 5.8 deaths per 1,000 standard population between 1998 and 2008, resulting in the ACT consistently having one of the lowest standardised death rates of the states and territories. In comparison, the standardised death rate for Australia decreased from 7.2 deaths to 6.0 deaths per 1,000 standard population over the same period.
DEATHS, Summary statistics: Australian Capital Territory |
|
 |  |  | 1998 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 |
|
| Deaths of usual residents of the ACT |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 | Registered in the ACT | no. | 1 202 | 1 438 | 1 419 | 1 545 | 1 646 |
 | Registered elsewhere in Australia | no. | 70 | 53 | 65 | 52 | 51 |
 | Total | no. | 1 272 | 1 491 | 1 484 | 1 597 | 1 697 |
| Standardised death rate(a) | rate | 6.6 | 5.7 | 5.5 | 5.6 | 5.8 |
| Life expectancy at birth |  |  |  |  |  |  |
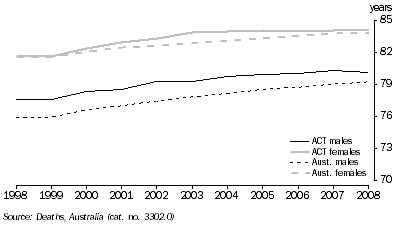
 | Males | years | 77.5 | 79.9 | 80.0 | 80.3 | 80.1 |
 | Females | years | 81.6 | 84.0 | 83.9 | 84.0 | 84.0 |
| Median age at death |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 | Males | years | 72.7 | 75.3 | 76.0 | 76.6 | 78.1 |
 | Females | years | 78.8 | 82.0 | 82.6 | 82.4 | 83.0 |
| Deaths registered in the ACT |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 | Resident of the ACT | no. | 1 202 | 1 438 | 1 419 | 1 545 | 1 646 |
 | Resident elsewhere in Australia | no. | 220 | 260 | 237 | 236 | 285 |
 | Total | no. | 1 422 | 1 698 | 1 656 | 1 781 | 1 931 |
|
| (a) Deaths per 1,000 standard population. Standardised death rates use total persons in the 2001 Australian population as the standard population. |
| Source: Deaths, Australia (cat. no. 3302.0); ABS data available on request, Deaths collection. |
Life expectancy
Life expectancy refers to the average number of additional years a person of a given age and sex might expect to live if the age-specific death rates of the given period continued throughout his/her lifetime. For additional reference, refer to the
Deaths, Australia (cat. no. 3302.0).
Life expectancy at birth for boys born in the ACT in 2006-2008 was 80.1 years, while life expectancy for girls was 84.0 years. This was higher than the national average for both sexes. Nationally, life expectancy at birth increased between 1998 and 2008 by 3.3 years to 79.2 years for males and by 2.2 years to 83.7 for females.
LIFE EXPECTANCY AT BIRTH, Australian Capital Territory and Australia
- 1998-2008
Causes of death
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is the international standard classification for epidemiological purposes and is designed to promote international comparability in the collection, processing, classification, and presentation of causes of death statistics. The classification is used to classify diseases and causes of disease or injury as recorded on many types of medical records as well as death records. The ICD has been revised periodically to incorporate changes in the medical field. Currently ICD 10th revision is used for Australian causes of death statistics. Refer to
Causes of Death, Australia (cat. no. 3303.0) for additional details.
According to
Causes of Death, Australia, the four main causes of death for ACT residents in 2007 were Neoplasms (C00-D48); Diseases of the circulatory system (I00-I99); External causes (V01-Y98) and Diseases of the respiratory system (J00-J99).
Of all deaths registered in the ACT, 31.6% or 504 were caused by neoplasms (cancer) (C00-D48). Cancer of the digestive organs (C15-C26) accounted for 31.0% of all neoplasms, followed by respiratory and intrathoracic cancer (C30-C39) with 16.9%.
Diseases of the circulatory system (e.g. heart disease and cerebrovascular disease i.e. stroke) (I00-I99) accounted for 494 or 30.9% of all deaths in the ACT. This was followed by External causes of morbidity and mortality (e.g. accidents, poisoning and violence) (V01-Y98) which accounted for 114 or 7.1% and Diseases of the respiratory system (J00-J99) with 104 or 6.5%.
End note:
1. United Nations,
Economic and Social Council, Statistical Commission Thirtieth Session, E/CN.3/1999/10, p.13, United Nations, 1-5 March 1999.
 Print Page
Print Page