MEASURING DIABETES - DEFINITIONS
In the National Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Health Measures Survey (NATSIHMS), two blood tests for diabetes were performed: fasting plasma glucose and glycated haemoglobin (commonly referred to as HbA1c). The tables available on the Downloads page of this publication present diabetes prevalence rates for both tests, including a comparison of the two tests in Table 6. However, at the time of publication, fasting plasma glucose is still the current standard test for diabetes in Australia, therefore the results presented in the publication commentary focus on fasting plasma glucose only.
Diabetes prevalence was derived using a combination of blood test results and self-reported information on diabetes diagnosis and medication use.
A person was considered to have known diabetes if:
- they had ever been told by a doctor or nurse that they have diabetes and they were taking diabetes medication (either insulin or tablets); OR
- they had ever been told by a doctor or nurse that they have diabetes and their blood test result for fasting plasma glucose was greater than or equal to the cut off point for diabetes (that is, ≥7.0 mmol/L).
Note: people who had been told by a doctor or nurse that they have diabetes, but who were not taking medication for diabetes and did not have a fasting plasma glucose level ≥7.0 mmol/L, were classified as not having diabetes.
People with known diabetes were further classified as having Type I, Type II or Type unknown, based on the type of diabetes that a doctor or nurse told them they had. Women with gestational diabetes were excluded.
- A person was considered to have newly diagnosed diabetes if they reported no prior diagnosis of diabetes but had a fasting plasma glucose value ≥7.0 mmol/L.
Total persons with diabetes was defined as the total of known diabetes and newly diagnosed diabetes.
- A person was considered to be at high risk of diabetes if they did not currently have diabetes, but had an impaired fasting plasma glucose result, that is, a fasting plasma glucose level ranging from 6.1 mmol/L to less than 7.0 mmol/L.1
The NATSIHMS diabetes classification is outlined in Figure 1 (this is also the same classification used for the general population). More information on diabetes prevalence is presented in Tables 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 17 on the Downloads page of this publication.
Information on diabetes prevalence using this same definition but based on HbA1c test results are also shown in Tables
1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 17. The relevant cut-offs for HbA1c are as follows:
- Indicates diabetes: ≥6.5%
- At high risk of diabetes: 6.0% to <6.5%
- Does not indicate diabetes: <6.0%.
Figure 1: 2012–13 NATSIHMS diabetes classification
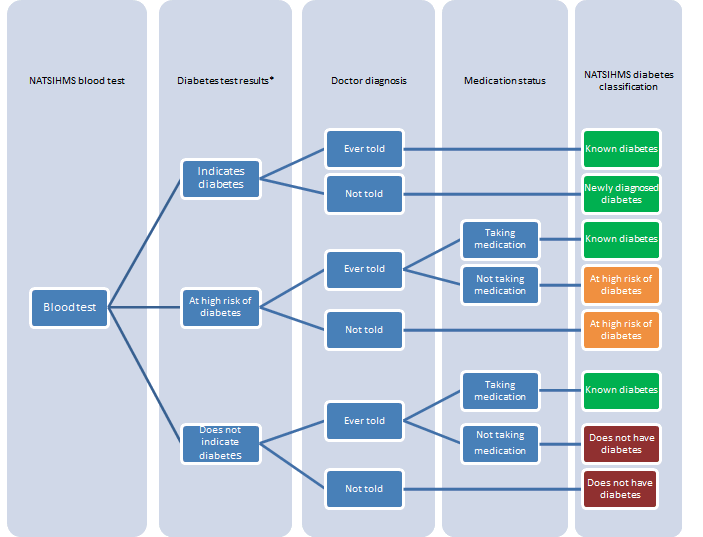 * Cut-offs for FPG: Indicates diabetes ≥7.0 mmol/L; At high risk of diabetes 6.1 to <7.0 mmol/L; Does not indicate diabetes <6.1 mmol/L.
*Cut-offs for HbA1c: Indicates diabetes ≥6.5%; At high risk of diabetes 6.0% to <6.5%; Does not indicate diabetes <6.0%.
* Cut-offs for FPG: Indicates diabetes ≥7.0 mmol/L; At high risk of diabetes 6.1 to <7.0 mmol/L; Does not indicate diabetes <6.1 mmol/L.
*Cut-offs for HbA1c: Indicates diabetes ≥6.5%; At high risk of diabetes 6.0% to <6.5%; Does not indicate diabetes <6.0%.
ENDNOTES
1 World Health Organization 2006,
Definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycemia, <
http://www.who.int/diabetes/publications/Definition%20and%20diagnosis%20of%20diabetes_new.pdf>,
Back to top
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All