EDUCATION
Education contributes to individual wellbeing and economic growth. Higher levels of educational attainment are associated with increased employment opportunities and higher wages, and contribute to improving Australia's economic standing. The changing structure and growth of the Australian economy has increased the demand for a diverse, skilled workforce, with higher levels of educational attainment required to meet this demand.
Level of highest educational attainment
The indicator of educational progress used in this chapter measures the attainment of formal non-school qualifications. The statistics relating to educational attainment relate to people aged 15 years and over.
In 2006, more than one-third (34%) of the 1.6 million people aged 15 years and over living in the MDB held at least one non-school qualification (as reported in the Census), lower than the national rate of 37% (table 2.12). Of these, more than 204,000 people held a Bachelor degree or higher, 96,000 people held an Advanced diploma or Diploma, and 240,000 people held a Certificate level qualification - a group which includes the traditional trade qualifications.
2.12 Level of highest non-school qualification(a) - 2006 |
|  |
 |  | Murray-Darling Basin | Australia |  |
 |  | Population | Proportion of total persons | Population | Proportion of total persons |  |
 |  | no. | % | no. | % |  |
|  |
| With non-school qualification |  |  |  |  |  |
 | Postgraduate degree | 31 960 | 2.0 | 412 270 | 2.6 |  |
 | Graduate diploma and Graduate certificate | 25 130 | 1.6 | 228 150 | 1.4 |  |
 | Bachelor degree | 146 970 | 9.3 | 1 836 610 | 11.6 |  |
 | Advanced diploma and Diploma | 96 140 | 6.1 | 1 128 220 | 7.1 |  |
 | Certificate | 240 270 | 15.2 | 2 284 590 | 14.4 |  |
 | Total | 540 470 | 34.1 | 5 889 840 | 37.1 |  |
| Without non-school qualification | 835 700 | 52.7 | 7 760 700 | 48.9 |  |
| Total persons aged 15 years and over(b) | 1 583 390 | 100.0 | 15 879 920 | 100.0 |  |
|  |
| (a) Persons aged 15 years and over. |
| (b) Includes persons who did not state or inadequately described their qualifications. |
| Source: ABS data available on request, ABS Census on Population and Housing, 2006 |
As with Australia, the educational attainment of people living in the MDB has increased over the last decade. Between 1996 and 2006 the number of people holding a non-school qualification increased by 36%. The increase mostly reflected the increase in the proportion of people whose level of highest non-school qualification was a Bachelor degree or higher which increased by 42% since 1996 (compared to a 57% rise for Australia).
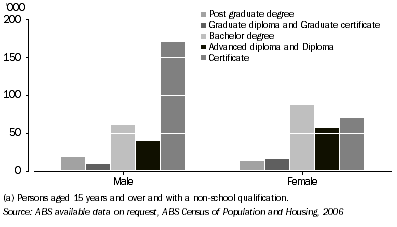
In 2006, more males than females in the MDB held a non-school qualification (38% and 30% respectively), although females were more likely to have a Bachelor degree or higher than males (14% and 11% respectively). The most common level of highest non-school qualification held by males was a Certificate (22%) (graph 2.13).
2.13 Level of Highest non-school qualification(a), by sex-Murray-Darling Basin-2006
Field of study
The most common fields of study of people in the MDB with a non-school qualification were Engineering and related technologies (20%), Management and commerce (14%) and Society and culture (12%). While Agriculture was not as common (4%), its proportion in the MDB was much higher than the national rate (1%) (table 2.14).
2.14 Selected fields of study(a) - 2006 |
|  |
 | Murray-Darling Basin | Australia |  |
 | Number | Proportion of total persons(a) | Number | Proportion of total persons(a) |  |
 | no. | % | no. | % |  |
|  |
| Engineering and related technologies | 107 530 | 19.9 | 1 259 300 | 21.4 |  |
| Management and commerce | 74 130 | 13.7 | 1 026 610 | 17.4 |  |
| Society and culture | 65 980 | 12.2 | 659 980 | 11.2 |  |
| Education | 61 570 | 11.4 | 584 180 | 9.9 |  |
| Health | 60 300 | 11.2 | 604 850 | 10.3 |  |
| Agriculture | 18 730 | 3.5 | 59 480 | 1.0 |  |
| Horticulture and viticulture | 6 920 | 1.3 | 53 150 | 0.9 |  |
| Other fields of study(b) | 145 300 | 26.9 | 1 642 290 | 27.9 |  |
Total persons with a non-school
qualification(c) | 540 470 | 100.0 | 5 889 840 | 100.0 |  |
|  |
| (a) Persons aged 15 years and over and with a non-school qualification. |
| (b) Includes Natural and physical sciences, Information technology, Architecture and building, Other agriculture, environmental and related sciences etc. |
| (c) Components may not add to total due to rounding. |
| Source: ABS data available on request, ABS Census of Population and Housing, 2006 |
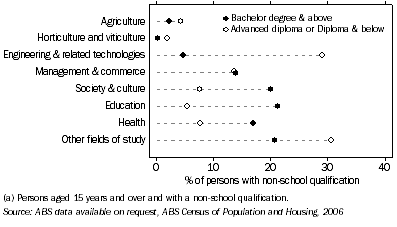
The level of qualification attained by people varies depending on their field of study. Some fields of study are more likely to result in Bachelor degrees, however, other fields were more likely to result in Certificate or Diploma level qualifications (graph 2.15). For people whose highest non-school qualification was a Bachelor degree or higher, the most common fields of study were Education (21%), Society and culture (20%), Health (17%) and Management and commerce (14%). For those with Certificate and Diploma level qualifications, the most common field of study was Engineering and related studies (29%); followed by Management and commerce (14%). There were more holders of Certificates/Diplomas (4%) than Bachelor degrees or higher (2%) who were educated in Agriculture.
2.15 Field of study(a), by highest non-school qualification
- Murray-Darling Basin - 2006
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All