BARRIERS TO INNOVATION
Understanding the barriers to innovation is important for policy makers, as it supports the targeting of resources and programs designed to encourage innovative activity. All businesses were asked to report whether any of the listed factors impacted on their ability to develop or introduce new goods, services, processes or methods. Businesses could select more than one of these factors and a ranking of importance was not required.
While the focus in this release is on innovation-active businesses and factors that influence innovation, the Business Characteristics Survey (BCS) collects a comprehensive range of factors that hamper the ability of a business to undertake innovation as well as factors which may impact on more general business activities or performance. The complete data for all businesses will be released as part of Selected Characteristics of Australian Business, 2010-11 (cat. no. 8167.0).
Barriers to innovation(a)(b)(c), by innovation status, 2009 - 10 and 2010 - 11 |
|
 |  | 2009-10 | 2010-11 |
 |  | Innovation-active businesses | Non innovation-active businesses | All businesses | Innovation-active businesses | Non innovation-active businesses | All businesses |
 |  | % | % | % | % | % | % |
|
| Lack of access to additional funds | 28.1 | 10.9 | 18.4 | 32.0 | 14.2 | 21.1 |
| Cost of development or introduction/implementation | 21.1 | 6.9 | 13.1 | 23.3 | 9.7 | 15.0 |
| Lack of skilled persons: |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 | within the business | 21.0 | 7.7 | 13.6 | 20.7 | 8.2 | 13.1 |
 | within the labour market | 18.2 | 9.2 | 13.2 | 17.5 | 9.2 | 12.5 |
 | in any location(d) | 29.2 | 13.5 | 20.4 | 29.8 | 13.7 | 20.0 |
| Lack of access to knowledge or technology to enable development or introduction/implementation | 6.2 | 1.9 | 3.8 | 6.5 | 1.7 | 3.6 |
| Government regulations and compliance | 20.3 | 10.0 | 14.5 | 16.5 | 10.8 | 13.0 |
| Adherence to standards | 7.7 | 3.3 | 5.2 | 5.9 | 2.9 | 4.1 |
| Uncertain demand for new goods or services | 19.8 | 8.4 | 13.4 | 18.7 | 9.0 | 12.8 |
| Any of the listed barriers to innovation | 62.7 | 30.4 | 44.6 | 63.1 | 33.3 | 44.9 |
| None of the listed barriers to innovation | 37.3 | 69.6 | 55.4 | 36.9 | 66.7 | 55.1 |
|
| (a) Proportions are of all businesses in each output category. |
| (b) Barriers to innovation are those barriers which significantly hampered the development or introduction of any new or significantly improved goods, services, processes and/or methods. |
| (c) Businesses could identify more than one barrier and were not asked to rank barriers in order of importance. |
| (d) Includes businesses that reported lack of skilled persons within the business and/or lack of skilled persons within the labour market. |
During the year ended 30 June 2011, the proportion of all businesses that reported any of the listed barriers to innovation was 45%, consistent with the previous year. Innovation-active businesses (63%) were almost twice as likely to report at least one of these barriers to undertaking innovative activity than non innovation-active businesses (33%).
Lack of access to additional funds as a barrier to innovation was reported by 32% of innovation-active businesses, an increase of four percentage points from the previous year. The proportion of innovation-active businesses which reported
government regulations and compliance as a barrier to innovation decreased four percentage points from 20% in 2009-10 to 16% in 2010-11.
INNOVATION-ACTIVE BUSINESSES, Barriers to innovation(a)(b)(c), by employment size, 2010 - 11 |
|
 |  | 0-4 persons | 5-19 persons | 20-199 persons | 200 or more persons | Total |
 |  | % | % | % | % | % |
|
| Lack of access to additional funds | 33.8 | 32.4 | 24.8 | 14.7 | 32.0 |
| Cost of development or introduction/implementation | 22.5 | 24.8 | 22.3 | 16.0 | 23.3 |
| Lack of skilled persons: |  |  |  |  |  |
 | within the business | 18.5 | 22.7 | 22.6 | 14.4 | 20.7 |
 | within the labour market | 13.9 | 19.9 | 23.7 | 17.0 | 17.5 |
 | in any location(d) | 26.5 | 32.8 | 33.0 | 24.4 | 29.8 |
| Lack of access to knowledge or technology to enable development or introduction/implementation | 7.2 | 6.9 | 3.1 | 4.5 | 6.5 |
| Government regulations and compliance | 15.4 | 17.6 | 17.5 | 7.7 | 16.5 |
| Adherence to standards | 5.2 | 6.3 | 7.7 | 2.3 | 5.9 |
| Uncertain demand for new goods or services | 18.1 | 20.1 | 16.9 | 8.9 | 18.7 |
| Any of the listed barriers to innovation | 62.7 | 64.9 | 60.1 | 42.8 | 63.1 |
| None of the listed barriers to innovation | 37.3 | 35.1 | 39.9 | 57.2 | 36.9 |
|
| (a) Proportions are of innovation-active businesses in each output category. |
| (b) Barriers to innovation are those barriers which significantly hampered the development or introduction of any new or significantly improved goods, services, processes and/or methods. |
| (c) Businesses could identify more than one barrier and were not asked to rank barriers in order of importance. |
| (d) Includes businesses that reported lack of skilled persons within the business and/or lack of skilled persons within the labour market. |
Of innovation-active businesses, those with 5-19 persons employed (65%) were most likely to report at least one of the listed barriers to the introduction of new goods, services, processes or methods, while those with 200 or more persons employed (43%) were least likely to report any of the listed barriers to innovation. Across all employment size ranges,
lack of access to additional funds was the most commonly reported barrier to innovation, with the exception of businesses with 200 or more persons employed which were most likely to report
lack of skilled persons within the labour market (17%) as a barrier to innovation.
The highest proportion of innovation-active businesses reporting
none of the listed barriers to undertaking innovation was recorded in Health care and social assistance (51%), followed by Mining (49%).
Proportion of innovation-active businesses which reported lack of access to additional funds as a barrier to innovation, by industry, 2010-11
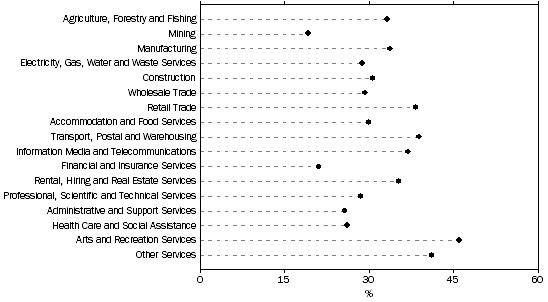
Lack of access to additional funds was the most commonly reported impediment to innovation for 15 out of 17 industries, with businesses in Arts and recreation services most likely to report this barrier (46%), followed by Other services (41%). Businesses in Mining were the least likely to report this barrier to innovation (19%).
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All