CONSUMER PRICE INDEX (CPI)
The description of the CPI commonly adopted by users is in terms of its perceived uses; hence the frequent references to the CPI as a measure of inflation, a measure of changes in purchasing power, or a measure of changes in the cost of living. The concept adopted in Australia for the CPI is a measure of changes, over time, in the prices of a basket of goods and services acquired by households in the eight capital cities in Australia. As such, the CPI has been designed as a general measure of price inflation for the household sector.
The simplest way of thinking about the CPI is to imagine a basket of goods and services of the kind typically acquired by Australian households. As prices vary, the total cost of this basket will also vary. The CPI is simply a measure of the changes in the cost of this basket as the prices of items in it change.
From the September quarter 2005 onwards, the total basket is divided into the following 11 major commodity groups: Food; Alcohol and tobacco; Clothing and footwear; Housing; Household contents and services; Health; Transportation; Communication; Recreation; Education; and Financial and insurance services. These groups are, in turn, divided into 33 subgroups and the subgroups into 90 expenditure classes.
In addition to the aggregate 'All groups' index, indexes are also compiled and published for each of the groups, subgroups and expenditure classes for each state capital city, Darwin and Canberra. National indexes are constructed as the weighted average of the indexes compiled for each of the eight capital cities.
The 15th Series CPI is the latest of a number of retail/consumer price indexes that have been constructed for various purposes by the ABS. (More information about the CPI can be found in Australian Consumer Price Index: Concepts, Sources and Methods (6461.0).)
Price movements by city
Table 29.1 presents All groups CPI numbers for each of the eight capital cities and for the weighted average of the eight capital cities, together with percentage changes.
29.1 CONSUMER PRICE INDEX, Capital cities(a) |
|  |
 | Sydney | Melbourne | Brisbane | Adelaide | Perth | Hobart | Darwin | Canberra | Weighted
average
of eight
capital
cities |  |
Index Number(b) |  |
|  |
| 2002-03 | 141.1 | 139.7 | 140.7 | 142.7 | 136.8 | 139.1 | 136.8 | 139.7 | 140.2 |  |
| 2003-04 | 144.1 | 142.8 | 144.8 | 147.0 | 139.6 | 142.6 | 138.7 | 143.4 | 143.5 |  |
| 2004-05 | 147.7 | 145.7 | 148.5 | 150.4 | 144.0 | 147.1 | 141.8 | 146.7 | 147.0 |  |
| 2005-06 | 152.1 | 150.2 | 153.2 | 155.2 | 150.1 | 151.8 | 146.5 | 151.9 | 151.7 |  |
| 2006-07 | 156.2 | 154.2 | 158.3 | 159.2 | 156.1 | 155.7 | 152.9 | 156.4 | 156.1 |  |
Change from previous financial year (%) |  |
|  |
| 2002-03 | 2.8 | 3.3 | 3.2 | 4.0 | 2.8 | 3.3 | 2.3 | 3.3 | 3.1 |  |
| 2003-04 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 2.9 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 1.4 | 2.6 | 2.4 |  |
| 2004-05 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 2.6 | 2.3 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 2.4 |  |
| 2005-06 | 3.0 | 3.1 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 4.2 | 3.2 | 3.3 | 3.5 | 3.2 |  |
| 2006-07 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 3.3 | 2.6 | 4.0 | 2.6 | 4.4 | 3.0 | 2.9 |  |
|  |
| (a) All group index numbers. Reference base year is 1989-90 = 100.0. |
| (b) Arithmetic average of quarterly index numbers for financial year. |
| Source: Consumer Price Index, Australia (6401.0). |
The capital city indexes measure price movements over time in each city individually. They can not be used to compare price levels between capital cities. For example, the index for Sydney in 2006-07 of 156.2, compared with the corresponding index for Darwin of 152.9, does not mean that prices in Sydney are higher than those in Darwin. It simply means, since the reference base period (1989-90), prices in Sydney have increased by a greater percentage than those in Darwin (56.2% compared with 52.9%).
Price movements by broad commodity group
Table 29.2 presents, for the weighted average of the eight capital cities, index numbers for each of the 11 major commodity groups of the 15th Series CPI and for All groups, together with percentage changes.
29.2 CONSUMER PRICE INDEX, Major commodity groups(a) |
|  |
 | Food | Alcohol
and
tobacco | Clothing
and
footwear | Housing | Household
contents
and
services | Health | Trans-
portation | Commun-
ication | Rec-
reation | Educa-
tion | Financial
and
insurance
services(b) | All groups |  |
Index Number(c) |  |
|  |
| 2002-03 | 147.9 | 208.9 | 113.3 | 115.1 | 121.0 | 181.5 | 140.6 | 108.5 | 131.9 | 210.0 | na | 140.2 |  |
| 2003-04 | 152.3 | 217.8 | 112.7 | 120.2 | 121.1 | 193.9 | 142.0 | 110.0 | 130.0 | 223.3 | na | 143.5 |  |
| 2004-05 | 154.8 | 225.4 | 110.8 | 124.8 | 120.7 | 204.3 | 146.8 | 111.1 | 130.7 | 238.7 | na | 147.0 |  |
| 2005-06 | 162.3 | 233.1 | 109.2 | 129.3 | 122.2 | 213.5 | 155.5 | 109.5 | 132.0 | 253.2 | 101.2 | 151.7 |  |
| 2006-07 | 172.4 | 240.6 | 108.4 | 133.7 | 124.6 | 223.5 | 158.0 | 110.8 | 133.8 | 264.6 | 103.0 | 156.1 |  |
Change from previous financial year (%) |  |
|  |
| 2002-03 | 3.6 | 2.9 | 0.8 | 3.6 | 1.1 | 6.8 | 2.4 | 3.1 | 2.6 | 5.0 | na | 3.1 |  |
| 2003-04 | 3.0 | 4.3 | -0.5 | 4.4 | 0.1 | 6.8 | 1.0 | 1.4 | -1.4 | 6.3 | na | 2.4 |  |
| 2004-05 | 1.6 | 3.5 | -1.7 | 3.8 | -0.3 | 5.4 | 3.4 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 6.9 | na | 2.4 |  |
| 2005-06 | 4.8 | 3.4 | -1.4 | 3.6 | 1.2 | 4.5 | 5.9 | -1.4 | 1.0 | 6.1 | na | 3.2 |  |
| 2006-07 | 6.2 | 3.2 | -0.7 | 3.4 | 2.0 | 4.7 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 4.5 | 1.8 | 2.9 |  |
|  |
| na not available |
| (a) Weighted average of the eight capital cities. Reference base year is 1989-90 = 100.0. |
| (b) The Financial and insurance service group was introduced in September quarter 2005 with a reference base of June quarter 2005 = 100.0. There are no historic data for this series. |
| (c) Arithmetic average of quarterly index numbers for financial year. |
| Source: Consumer Price Index, Australia (6401.0). |
Price movements for selected household types
Graph 29.3 and table 29.4 present analytical indexes specifically designed to measure changes in living costs for four selected household types: Employee households; Age pensioner households; Other government transfer recipient households; and Self-funded retiree households.
29.3 Analytical Living Cost Indexes for selected household types(a) - June 1999 to June 2007
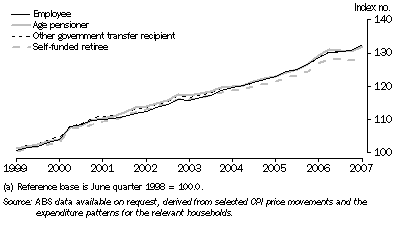
These indexes represent the conceptually preferred measures for assessing the impact of changes in prices on the disposable incomes of households. In other words, these indexes are particularly suited for assessing whether or not the disposable incomes of households have kept pace with price changes, that is whether living costs are being maintained. The CPI, on the other hand, is designed specifically to measure price inflation for the household sector as a whole and, as such, is not the conceptually ideal measure for assessing the impact of price changes on the disposable incomes of households. The most notable differences are that living cost indexes include interest charges but do not include house purchases, while inflation indexes do not include interest charges but do include house purchases.
29.4 ANALYTICAL LIVING COST INDEXES FOR SELECTED HOUSEHOLD TYPES(a) |
|  |
 | Employee | Age pensioner | Other government
transfer recipient | Self-funded retiree | CPI(b)(c) |  |
Index number(d) |  |
|  |
| 2002-03 | 114.9 | 116.3 | 115.9 | 115.2 | 115.9 |  |
| 2003-04 | 118.1 | 119.0 | 118.6 | 117.7 | 118.6 |  |
| 2004-05 | 121.7 | 121.8 | 121.6 | 120.3 | 121.5 |  |
| 2005-06 | 126.1 | 126.3 | 126.1 | 124.4 | 125.3 |  |
| 2006-07 | 131.0 | 131.1 | 130.9 | 128.4 | 129.0 |  |
Change from previous year (%) |  |
|  |
| 2002-03 | 3.3 | 3.2 | 3.1 | 3.3 | 3.1 |  |
| 2003-04 | 2.7 | 2.3 | 2.4 | 2.1 | 2.3 |  |
| 2004-05 | 3.0 | 2.3 | 2.6 | 2.2 | 2.4 |  |
| 2005-06 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.4 | 3.2 |  |
| 2006-07 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 2.9 |  |
|  |
| (a) Reference base is June quarter 1998 = 100.0. |
| (b) The CPI has been re-referenced from 1989-90 = 100.0 to June quarter 1998 = 100.0 for ease of comparison with the living cost indexes for household types. |
| (c) The CPI is designed to measure price inflation for the household sector and not changes in living costs. |
| (d) Annual average of quarterly index numbers. |
| Source: Analytical Living Cost Indexes for Selected Household Types (6463.0), data derived from selected CPI price movements and the expenditure patterns for the relevant households. |
For more information about these indexes see the article
Price impacts on the living costs of selected household types in
Year Book Australia 2005.
Between 2005-06 and 2006-07 changes in living costs ranged from a low of 3.3% for Self-funded retiree households to a high of 3.9% for Employee households. The CPI rose by 2.9% over the same period. Over the period from 1998-99 to 2006-07, changes in living costs for all four household types are similar to the change in the CPI. Changes in living costs ranged from 28.0% for Self-funded retiree households to 30.4% for Employee households. The CPI rose by 28.1%.
Long-term price series
Although the CPI has only been compiled from 1948, an approximate long-term measure of retail price change has been constructed by linking together earlier selected retail price index series (table 29.5). The index numbers are expressed on the reference base year 1945 = 100.0. The successive series are:
- from 1901 to 1914, the A series retail price index
- from 1914 to 1946-47, the C series retail price index
- from 1946-47 to 1948-49, a combination of the C series index (excluding rent) and the housing group of the CPI
- from 1948-49 onwards, the CPI.
For more information about these former retail price index series see the article
History of retail/consumer price indexes in Australia in
Year Book Australia 2005.
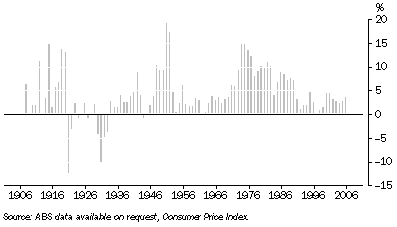
Graph 29.6 shows the annual percentage changes derived from this retail/consumer price index series for the period 1905-2006.
29.5 RETAIL/CONSUMER PRICE INDEX NUMBERS(a)(b) |
|  |
| Year | Index no. | Year | Index no. | Year | Index no. | Year | Index no. |  |
|  |
| 1901 | 47 | 1931 | 78 | 1961 | 252 | 1991 | 1 898 |  |
| 1902 | 50 | 1932 | 74 | 1962 | 251 | 1992 | 1 917 |  |
| 1903 | 49 | 1933 | 71 | 1963 | 252 | 1993 | 1 952 |  |
| 1904 | 46 | 1934 | 73 | 1964 | 258 | 1994 | 1 989 |  |
| 1905 | 48 | 1935 | 74 | 1965 | 268 | 1995 | 2 082 |  |
| 1906 | 48 | 1936 | 75 | 1966 | 276 | 1996 | 2 136 |  |
| 1907 | 48 | 1937 | 78 | 1967 | 286 | 1997 | 2 141 |  |
| 1908 | 51 | 1938 | 80 | 1968 | 293 | 1998 | 2 159 |  |
| 1909 | 51 | 1939 | 82 | 1969 | 302 | 1999 | 2 191 |  |
| 1910 | 52 | 1940 | 85 | 1970 | 313 | 2000 | 2 289 |  |
| 1911 | 53 | 1941 | 89 | 1971 | 332 | 2001 | 2 389 |  |
| 1912 | 59 | 1942 | 97 | 1972 | 352 | 2002 | 2 462 |  |
| 1913 | 59 | 1943 | 101 | 1973 | 385 | 2003 | 2 530 |  |
| 1914 | 61 | 1944 | 100 | 1974 | 443 | 2004 | 2 588 |  |
| 1915 | 70 | 1945 | 100 | 1975 | 510 | 2005 | 2 658 |  |
| 1916 | 71 | 1946 | 102 | 1976 | 579 | 2006 | 2 753 |  |
| 1917 | 75 | 1947 | 106 | 1977 | 650 |  |  |  |
| 1918 | 80 | 1948 | 117 | 1978 | 702 |  |  |  |
| 1919 | 91 | 1949 | 128 | 1979 | 766 |  |  |  |
| 1920 | 103 | 1950 | 140 | 1980 | 844 |  |  |  |
| 1921 | 90 | 1951 | 167 | 1981 | 926 |  |  |  |
| 1922 | 87 | 1952 | 196 | 1982 | 1 028 |  |  |  |
| 1923 | 89 | 1953 | 205 | 1983 | 1 132 |  |  |  |
| 1924 | 88 | 1954 | 206 | 1984 | 1 177 |  |  |  |
| 1925 | 88 | 1955 | 211 | 1985 | 1 257 |  |  |  |
| 1926 | 90 | 1956 | 224 | 1986 | 1 370 |  |  |  |
| 1927 | 89 | 1957 | 229 | 1987 | 1 487 |  |  |  |
| 1928 | 89 | 1958 | 233 | 1988 | 1 594 |  |  |  |
| 1929 | 91 | 1959 | 237 | 1989 | 1 714 |  |  |  |
| 1930 | 87 | 1960 | 245 | 1990 | 1 839 |  |  |  |
|  |
| na not available |
| (a) Reference base year is 1945 = 100.0. |
| (b) The index numbers from 1901 to 1980 relate to the weighted average of six state capital cities; and from 1981 to the weighted average of eight capital cities. Index numbers are for calendar years. |
| Source: ABS data available on request, Consumer Price Index. |
29.6 Retail/Consumer Price Index, annual changes
International comparisons
In analysing price movements in Australia, an important consideration is Australia's performance relative to other countries. However, due to the many differences in the structure of the housing sector in different countries and in the way housing is treated in their CPIs, a simple comparison of All groups (or 'headline') CPIs is often inappropriate. In order to provide a better basis for international comparisons, the Seventeenth International Conference of Labour Statisticians (2003) adopted a resolution which called for countries, where possible, to compile and provide for dissemination to the international community an index that excludes housing and financial services.
Table 29.7 presents indexes for selected countries on a basis consistent with the resolution and broadly comparable to the Australian series 'All groups excluding Housing and Financial and insurance services'.
29.7 CONSUMER PRICE INDEX, International comparisons(a)(b) |
|  |
 | 2002-03 | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 |  |
Index Numbers |  |
|  |
| Australia | 144.6 | 147.3 | 150.3 | 155.2 | 159.8 |  |
| Canada | 135.2 | 136.9 | 139.3 | 142.2 | 143.8 |  |
| Germany | 127.4 | 128.9 | 131.1 | 133.1 | 135.0 |  |
| Hong Kong | 159.0 | 158.5 | 161.2 | 162.6 | 164.7 |  |
| Indonesia | 495.8 | 524.4 | 560.2 | 646.6 | nya |  |
| Japan | 106.4 | 106.1 | 106.2 | 106.1 | nya |  |
| Korea, Republic of | 190.9 | 197.4 | 204.9 | 210.4 | 215.4 |  |
| New Zealand | 130.1 | 130.5 | 132.9 | 136.8 | 139.5 |  |
| Singapore | 122.4 | 124.2 | 125.6 | 126.9 | nya |  |
| Taiwan | 130.5 | 131.1 | 134.7 | 138.2 | 138.4 |  |
| United Kingdom | 145.8 | 147.9 | 149.7 | 152.8 | nya |  |
| United States of America | 138.9 | 141.8 | 146.2 | 152.6 | 155.6 |  |
Change from previous year (%) |  |
|  |
| Australia | 3.0 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 3.3 | 3.0 |  |
| Canada | 3.8 | 1.3 | 1.8 | 2.1 | 1.1 |  |
| Germany | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 1.4 |  |
| Hong Kong | -2.0 | -0.3 | 1.7 | 0.9 | 1.3 |  |
| Indonesia | 8.2 | 5.8 | 6.8 | 15.4 | nya |  |
| Japan | -1.2 | -0.3 | 0.1 | -0.1 | 0.1 |  |
| Korea, Republic of | 3.2 | 3.4 | 3.8 | 2.7 | 2.4 |  |
| New Zealand | 1.9 | 0.3 | 1.8 | 2.9 | 2.0 |  |
| Singapore | 0.4 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 1.0 | nya |  |
| Taiwan | -0.1 | 0.5 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 0.1 |  |
| United Kingdom | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 2.1 | nya |  |
| United States of America | 1.8 | 2.1 | 3.1 | 4.4 | 2.0 |  |
|  |
| nya not yet available |
| (a) Reference base year is 1989-90 = 100.0. |
| (b) All groups excluding Housing and Financial and insurance services. |
| Source: Consumer Price Index, Australia (6401.0). |
 Print Page
Print Page