JULY KEY FIGURES
 | May 2006 | June 2006 | July 2006 | Jun 06 to Jul 06 |  |
 | $m | $m | $m | % change |  |
TREND |  |
|  |
| Balance on goods and services | -1 156 | -1 090 | -952 | . . |  |
| Credits (exports of goods & services) | 17 088 | 17 276 | 17 492 | 1 |  |
| Debits (imports of goods & services) | 18 244 | 18 366 | 18 444 | - |  |
SEASONALLY ADJUSTED |  |
|  |
| Balance on goods and services | -2 246 | -635 | -588 | . . |  |
| Credits (exports of goods & services) | 16 553 | 17 876 | 17 405 | -3 |  |
| Debits (imports of goods & services) | 18 799 | 18 511 | 17 993 | -3 |  |
|  |
| . . not applicable |
| - nil or rounded to zero (including null cells) |
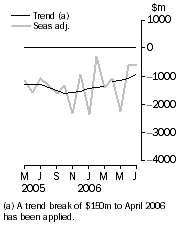
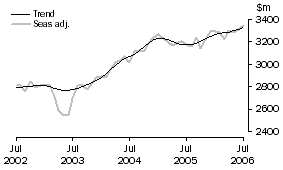
Balance on goods and services
|  |
JULY KEY POINTS
TREND ESTIMATES
- The provisional trend estimate of the balance on goods and services was a deficit of $952m in July 2006, a decrease of $138m on the revised deficit in June.
- Goods and services credits rose $216m (1%) to $17,492m. Goods and services debits rose $78m to $18,444m.
SEASONALLY ADJUSTED ESTIMATES
- In seasonally adjusted terms, the balance on goods and services was a deficit of $588m in July, a decrease of $47m on the revised deficit in June.
- Goods and services credits fell $471m (3%) to $17,405m. Non-rural and other goods fell $590m (5%), while rural goods rose $54m (2%). Services credits rose $65m (2%).
- Goods and services debits fell $518m (3%) to $17,993m. Intermediate and other goods fell $305m (4%) and capital goods fell $265m (8%), while consumption goods rose $12m. Services debits rose $40m (1%).
ORIGINAL ESTIMATES
- In original terms, the July balance on goods and services was a deficit of $107m, a decrease of $817m on the revised deficit in June. Goods and services credits rose $44m and goods and services debits fell $773m (4%).
- Non-rural and other goods were up $2.0b (19%) and rural goods were up $0.1b (5%) on the corresponding period in 2004-05.
NOTES
FORTHCOMING ISSUES
| ISSUE | Release Date |
| August 2006 | 4 October 2006 |
| September 2006 | 2 November 2006 |
| October 2006 | 29 November 2006 |
| November 2006 | 10 January 2007 |
| December 2006 | 2 February 2007 |
| January 2007 | 6 March 2007 |
CHANGES IN THIS ISSUE
In processing the 1 July 2006 changes made by the Australian Customs Service to the Harmonized Tariff, an error was discovered in concordances between two tariff item statistical codes and the detailed SITC and BoPBEC classifications. The error has been corrected from 1 July 2006. The error does not impact on data on a balance of payments basis but will result in a break in the imports series between June and July 2006 for the following items on a merchandise trade basis:
- SITC 33411 - Motor Spirit (incl. gasoline)
- SITC 33419 - Light petroleum/bituminous oils (excl. crude); light preparations, nes
- BoPBEC OK02 - Motor Spirit
- BoPBEC OK03 - Other Petroleum Products
INFORMATION PAPER
An information paper Proposed classification changes from 1 January 2007 to statistical codes of the Australian Harmonized Export Commodity Classification and the Customs Tariff (cat no. 5368.0.55.007) was released on 8 September 2006. The paper outlines the proposed changes to export and import statistical codes that will occur on 1 January 2007 as result of an update to the international Customs Tariff. As they become available, chapters of each classification will be added to the information paper, accessible from the details tab of this publication on the ABS web site www.abs.gov.au.
INQUIRIES
For further information about these and related statistics, contact the National Information and Referral Service on 1300 135 070 or Olivia Lam on Canberra (02) 6252 5540.
ANALYSIS AND COMMENTS
BALANCE ON GOODS AND SERVICES
The trend estimate of the balance on goods and services in July 2006 was a deficit of $952m, a decrease of $138m on the deficit in June.
In seasonally adjusted terms, the balance on goods and services in July 2006 was a deficit of $588m, a decrease of $47m on the deficit in June.
EXPORTS OF GOODS AND SERVICES
The trend estimate of goods and services credits rose $216m (1%) between June and July to $17,492m.
In seasonally adjusted terms, goods and services credits fell $471m (3%) to $17,405m. Other goods fell $413m (29%), non-rural goods fell $177m (2%), while rural goods rose $54m (2%). Services credits rose $65m (2%).
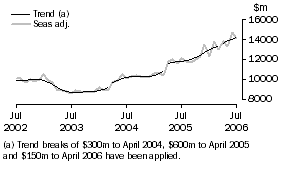
Exports of goods
GOODS CREDITS
RURAL GOODS
The trend estimate of rural goods exports rose $5m to $2,181m.
In seasonally adjusted terms, exports of rural goods rose $54m (2%) to $2,215m.
The movements in the seasonally adjusted components contributing to this rise were:
- cereal grains and cereal preparations, up $22m (5%)
- wool and sheepskins, up $16m (7%)
- other rural, up $16m (2%).
In original terms, exports of rural goods rose $31m (1%) to $2,206m.
NON-RURAL GOODS
The trend estimate of non-rural goods exports rose $181m (2%) to $10,790m.
In seasonally adjusted terms, exports of non-rural goods fell $177m (2%) to $10,878m.
The main movements in the seasonally adjusted components contributing to the fall were:
- metal ores and minerals, down $259m (8%)
- transport equipment, down $89m (22%).
Partly offsetting these effects were:
- other manufactures, up $79m (6%)
- other mineral fuels, up $63m (5%)
- metals (excluding non-monetary gold), up $23m (2%).
In original terms, exports of non-rural goods rose $109m (1%) to $11,271m.
The main movement in the original series contributing to the fall in seasonally adjusted terms was:
- transport equipment, down $136m (32%), compared to an average June to July fall of 4% over the previous three years, of which:
- road vehicles, down $99m (31%)
- other transport equipment, down $37m (32%).
OTHER GOODS
The trend estimate of other goods exports rose $26m (2%) to $1,249m.
In seasonally adjusted terms, exports of other goods fell $413m (29%) to $1,012m.
The main component contributing to the fall in the seasonally adjusted series was non-monetary gold, down $401m (33%).
In original terms, exports of other goods fell $420m (29%) to $1,004m.
Exports of services
SERVICES CREDITS
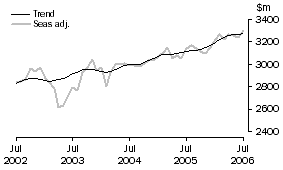
In trend terms, services credits rose $4m to $3,272m.
Seasonally adjusted, services credits rose $65m (2%) to $3,300m.
All components contributed to the rise in the seasonally adjusted series with:
- other services, up $32m (4%)
- transportation services, up $18m (3%)
- travel services, up $15m (1%).
Seasonally adjusted, tourism related services credits rose $31m (2%) to $2,097m.
IMPORTS OF GOODS AND SERVICES
The trend estimate of goods and services debits rose $78m between June and July to $18,444m.
In seasonally adjusted terms, goods and services debits fell $518m (3%) to $17,993m. Intermediate and other merchandise goods fell $309m (5%) and capital goods fell $265m (8%), while consumption goods rose $12m and other goods rose $4m (1%). Services debits rose $40m (1%).
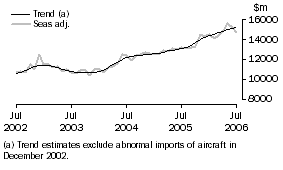
Imports of goods
GOODS DEBITS
CONSUMPTION GOODS
The trend estimate of imports of consumption goods rose $41m (1%) to $4,442m.
In seasonally adjusted terms, imports of consumption goods rose $12m to $4,428m.
The components contributing to the rise in the seasonally adjusted estimates were:
- consumption goods n.e.s., up $49m (4%)
- food and beverages, mainly for consumption, up $18m (3%)
- textiles, clothing and footwear, up $6m (1%).
Partly offsetting these effects were:
- non-industrial transport equipment, down $43m (4%)
- household electrical items, down $12m (3%)
- toys, books and leisure goods, down $6m (2%).
In original terms, imports of consumption goods rose $101m (2%) to $4,388m.
CAPITAL GOODS
The trend estimate of imports of capital goods fell $54m (2%) to $3,247m.
In seasonally adjusted terms, imports of capital goods fell $265m (8%) to $3,082m.
The main components contributing to the fall in the seasonally adjusted estimates were:
- industrial transport equipment n.e.s., down $102m (24%)
- civil aircraft, down $100m
- machinery and industrial equipment, down $72m (6%).
In original terms, imports of capital goods fell $597m (16%) to $3,035m.
INTERMEDIATE AND OTHER MERCHANDISE GOODS
The trend estimate of imports of intermediate and other merchandise goods rose $62m (1%) to $6,639m.
In seasonally adjusted terms, intermediate and other merchandise goods imports fell $309m (5%) to $6,421m.
The main components contributing to the fall in the seasonally adjusted estimates were:
- fuels and lubricants, down $429m (19%)
- primary industrial supplies n.e.s., down $45m (32%)
- parts for ADP equipment, down $19m (11%).
Partly offsetting these effects were:
- organic and inorganic chemicals, up $83m (29%)
- parts for transport equipment, up $46m (7%)
- processed industrial supplies n.e.s., up $27m (2%)
- other parts for capital equipment, up $18m (2%).
In original terms, imports of intermediate and other merchandise goods fell $445m (7%) to $6,274m.
OTHER GOODS
The trend estimate of imports of other goods rose $14m (2%) to $794m.
In seasonally adjusted terms, other goods imports rose $4m (1%) to $712m.
The main components contributing to the small rise in the seasonally adjusted estimates were:
- goods for processing, up $115m
- goods procured in ports by carriers, up $7m (6%).
Largely offsetting these effects was non-monetary gold, down $120m (21%).
In original terms, other goods imports rose $9m (1%) to $716m.
Imports of services
SERVICES DEBITS
In trend terms, services debits rose $15m to $3,322m.
Seasonally adjusted, services debits rose $40m (1%) to $3,350m.
All components contributed to the rise in the seasonally adjusted series with:
- travel services, up $32m (3%)
- other services, up $6m (1%)
- transportation services, up $2m.
Seasonally adjusted, tourism related services debits rose $27m (2%) to $1,747m.
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All