INTRODUCTION
Perinatal deaths comprise stillbirths, known as foetal deaths, and deaths of infants within the first 28 days of life, known as neonatal deaths. In this publication, and in previous editions since 1997, these deaths are defined to include infants and fetuses weighing at least 400 grams or having a gestational age of 20 weeks.
Care should be taken in using and interpreting perinatal deaths data contained in this publication due to the small numbers. In addition, only limited data is available for perinatal deaths in 2006. For further information refer to Explanatory Notes 59 and 70.
TRENDS IN PERINATAL DEATHS
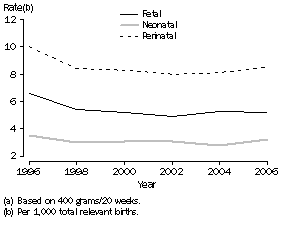
The perinatal death rate has remained at 8.5 deaths per 1,000 total relevant births from 2005 to 2006 (see Glossary, death rates for further information).
In 2006, there were 2,258 perinatal deaths registered in Australia, compared with 2,213 registered in 2005. The number of foetal deaths in 2006 was 1,394, a decrease of 1.2% on the number registered in 2005 (1,411). Neonatal deaths have increased 7.7% from 802 in 2005 to 864 in 2006. Compared with 1997, the number of registered perinatal deaths is 2.7% higher (63).
In 2006, there were 1,239 male perinatal deaths and 1,019 female perinatal deaths. The sex ratio was 121 male perinatal deaths for every 100 female perinatal deaths, compared with 117 males per 100 females in 2005.
The perinatal death rate was higher ten years ago in 1997 at 9.2 per 1,000 total relevant births. From 1997 to 2006, the foetal rate decreased from 6.0 to 5.2 per 1,000 total relevant births and the neonatal rate increased from 3.2 to 3.3 deaths per 1,000 total relevant births.
4.1 Trends in Perinatal Deaths (a)
CONDITION IN FOETUS/INFANT
In 2006, one in three (33%) of all perinatal deaths were not assigned a specific cause of death in the foetus/infant. Most of these were foetal deaths. While 47% of all foetal deaths registered in 2006 reported no specific cause, the corresponding figure for neonatal deaths was 21%.
Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities (Q00-Q99) accounted for 15% of perinatal deaths, while Respiratory and cardiovascular disorders specific to the perinatal period (P20-P29) contributed a further 8.6% and Disorders related to length of gestation and foetal growth (P05-P08) contributed 30%.
CONDITION IN THE MOTHER
Perinatal deaths differ from general deaths because a condition may be reported in the record for the fetus/infant, the mother, or for both. A maternal condition was reported in 1,670 (74%) of the 2,258 perinatal deaths registered in 2006. Maternal complications of pregnancy (P01) was the most frequently reported maternal cause, accounting for 859 or 38% of all perinatal deaths, followed by Complications of placenta, cord and membranes (P02) which accounted for 205 or 9.1% of perinatal deaths.
4.2 Foetal, Neonatal and Perinatal Deaths, 400 grams/20 weeks(a) - 1997-2006 |
|  |
 | FOETAL DEATHS | NEONATAL DEATHS | PERINATAL DEATHS |  |
| Year | Males | Females | Persons | Males | Females | Persons | Males | Females | Persons |  |
NUMBER |  |
|  |
| 1997 | 829 | 687 | 1 516 | 443 | 362 | 805 | 1 272 | 1 049 | 2 321 |  |
| 1998 | 707 | 629 | 1 336 | 435 | 319 | 754 | 1 142 | 948 | 2 090 |  |
| 1999 | 682 | 602 | 1 284 | 510 | 339 | 849 | 1 192 | 941 | 2 133 |  |
| 2000 | 692 | 611 | 1 303 | 443 | 330 | 773 | 1 135 | 941 | 2 076 |  |
| 2001 | 686 | 604 | 1 290 | 484 | 318 | 802 | 1 170 | 922 | 2 092 |  |
| 2002 | 682 | 558 | 1 240 | 426 | 353 | 779 | 1 108 | 911 | 2 019 |  |
| 2003 | 701 | 587 | 1 288 | 414 | 318 | 732 | 1 115 | 905 | 2 020 |  |
| 2004 | 732 | 615 | 1 347 | 418 | 283 | 701 | 1 150 | 898 | 2 048 |  |
| 2005 | 741 | 670 | 1 411 | 453 | 349 | 802 | 1 194 | 1 019 | 2 213 |  |
| 2006 | 747 | 647 | 1 394 | 492 | 372 | 864 | 1 239 | 1 019 | 2 258 |  |
RATES(b) |  |
|  |
| 1997 | 6.4 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 3.4 | 3.0 | 3.2 | 9.8 | 8.6 | 9.2 |  |
| 1998 | 5.5 | 5.2 | 5.4 | 3.4 | 2.6 | 3.0 | 8.9 | 7.8 | 8.4 |  |
| 1999 | 5.4 | 5.0 | 5.2 | 4.0 | 2.8 | 3.4 | 9.4 | 7.7 | 8.6 |  |
| 2000 | 5.4 | 5.0 | 5.2 | 3.5 | 2.7 | 3.1 | 8.9 | 7.7 | 8.3 |  |
| 2001 | 5.4 | 5.0 | 5.2 | 3.8 | 2.6 | 3.3 | 9.3 | 7.7 | 8.5 |  |
| 2002 | 5.3 | 4.6 | 4.9 | 3.3 | 2.9 | 3.1 | 8.6 | 7.4 | 8.0 |  |
| 2003 | 5.4 | 4.8 | 5.1 | 3.2 | 2.6 | 2.9 | 8.6 | 7.4 | 8.0 |  |
| 2004 | 5.6 | 5.0 | 5.3 | 3.2 | 2.3 | 2.8 | 8.8 | 7.3 | 8.1 |  |
| 2005 | 5.6 | 5.3 | 5.4 | 3.4 | 2.8 | 3.1 | 9.0 | 8.1 | 8.5 |  |
| 2006 | 5.5 | 5.0 | 5.2 | 3.6 | 2.9 | 3.3 | 9.1 | 7.9 | 8.5 |  |
|  |
| (a) See Explanatory notes, paragraphs 6-10 for further information |
| (b) Rates are per 1,000 total relevant births. See Glossary for further information. |
DATACUBES
Further information on perinatal deaths is presented in the datacubes associated with this publication.