Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Commission (ATSIC) region
An ATSIC region is a legally prescribed area for the purposes of administration by ATSIC and the Torres Strait Regional Authority. ATSIC regions can cross state or territory borders. For example, the ATSIC region of Queanbeyan crosses the borders of NSW, the ACT and Jervis Bay Territory (which is part of Other Territories). Reference: Population Distribution, Indigenous Australians (cat. no. 4705.0).
ABSTUDY
ABSTUDY payment consists of a fortnightly living allowance as well as additional components paid to indigenous students to assist with the costs associated with attending school. Reference: Centrelink.
Age-specific death rate
The number of deaths (occurred or registered) during the calendar year at a specified age per 1,000 of the estimated resident population of the same age at 30 June. Pro rata adjustment is made in respect of deaths for which the age of the deceased is not given. Reference: Deaths, Australia (cat. no. 3302.0).
Age-specific fertility rate
The number of live births (occurred or registered) during the calendar year, according to the age of mother, per 1,000 of the female resident population of the same age at 30 June. Pro rata adjustment is made for births for which the age of mother is not given. Reference: Births, Australia (cat. no. 3301.0).
Alcohol risk level
Risk levels were determined by the estimated average daily alcohol consumption in the 7 days prior to interview. Average daily consumption in the previous 7 days was estimated using two components: the number of days on which the respondent reported consuming alcohol in the previous week; and, the quantity consumed on the three most recent days on which they consumed alcohol in the past week. Risk levels are based on the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) risk levels for harm in the long term.
Reference: National Health Survey: Summary of Results (cat. no. 4364.0).
Australian and New Zealand Standard Industrial Classification (ANZSIC)
A classification of businesses by type of activity. Reference: Australian and New Zealand Standard Industrial Classification 1993 (cat. no. 1292.0).
Apparent retention rate
This is the number of school students in a designated level/year of education expressed as a percentage of their respective cohort group (which is either at the commencement of their secondary schooling or Year 10). In this publication, apparent retention rates are generally calculated for full-time school students who continued to Year 12 of secondary schooling. Reference: Schools, Australia (cat. no. 4221.0).
Assistance for Isolated Children Scheme (AIC)
A family payment for those with children attending primary, secondary education, or have an under 16 year old tertiary student who cannot go to an appropriate government school because of distance constraints. Reference: Centrelink.
Average annual growth rate
The average annual growth rate, r, is calculated as a percentage using the formula:
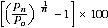
where P0 is the population at the start of the period, Pn is the population at the end of the period and n is the length of the period between Pn and P0 in years. Reference: Australian Demographic Statistics (cat. no. 3101.0).
Austudy
Austudy payments provide financial help to those who are aged 25 years or more who are studying full-time.
Reference: Centrelink.
Australia's Register of the National Estate
Australia’s national register of places of natural, historical and indigenous significance. Reference: Australia's State of the Forests Report, 2003, Bureau of Rural Sciences.
Average loan
The average loan series is calculated using the total value of lending commitments per month and the total number of dwellings financed per month. The average loan series does not necessarily represent the average loan size per dwelling. Reference: Housing Finance, Australia (cat. no. 5609.0).
Average takings per room night occupied
The takings from accommodation divided by the total number of room nights occupied for the survey period.
Reference: Tourist Accommodation, Australia (cat. no. 8635.0).
Balancing item
Calculated as the residual of Gross State Product (GSP) less state final demand less international trade in exports of goods and services, plus international trade in imports of goods and services. The balancing item implicitly comprises changes in inventories, total net interstate trade and a statistical discrepancy. Reference: Australian National Accounts: State Accounts (cat. no. 5220.0).
Birth
The delivery of a child, irrespective of the duration of the pregnancy, who, after being born, breathes or shows any other evidence of life such as heartbeat. Reference: Births, Australia (cat. no. 3301.0).
Blended family
A couple family containing two or more children aged 0-17 years, of whom at least one is the natural or adopted child of both members of the couple, and at least one is the step child of either member of the couple. Blended families may also include other children who are not the natural children of either parent.
Reference: Family Characteristics, Australia (cat. no. 4442.0).
Body Mass Index (BMI)
A measure calculated from self-reported height and weight data. The formula is weight (kg) divided by the square of height (m). To produce a measure of the prevalence of overweight or obesity in adults, BMI values are grouped in a way which allows categories to be reported against NHMRC guidelines. Reference: National Health Survey: Summary of Results (cat. no. 4364.0).
Bond/recognizance
There are several different types of bonds which may be imposed by a court. Generally speaking they all require the offender to be 'of good behaviour' for a certain length of time and may impose other conditions as well. Common conditions include that the offender:
- report to the Probation and Parole Service on a regular basis (bond with supervision);
- attend alcohol counselling;
- reside in a certain area.
Reference: NSW Criminal Courts Statistics 2003, Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research.
Bridging data
Data produced taking into account the quantification of differences in the scope of (usually) consecutive survey population characteristics, thus enabling serial analysis of selected data items. Reference: Australian Industry (cat. no. 8155.0).
Care and protection order
Care and protection orders can be grouped into four categories:
- guardianship orders involves the transfer of legal guardianship to an authorised department or to an individual
- custody orders refer to a third party being responsible for the day-to-day requirements of the child while the parent retains guardianship
- supervisory orders require authorised departments to supervise the level of care provided to the child
- interim and temporary orders provide for a limited period of supervision and/or placement of a child.
Reference: Child protection Australia 2003-04, Australian Institute of Health and Welfare.
Carer
A person of any age who provides any informal assistance, in terms of help or supervision, to persons with disabilities or long-term conditions, or older persons (i.e. aged 60 years and over). The assistance has to be ongoing, or likely to be ongoing, for at least six months. Reference: Disability, Ageing and Carers, Australia (cat. no. 4430.0).
Casualty
Any person killed or injured as a result of a crash. Reference: Road Traffic Accidents, 2003, Roads and Traffic Authority of NSW.
Chain volume measures
Estimates that exclude the direct effects of changes in prices. Unlike current measure estimates, they take account of changes to price relativities that occur from one year to the next. Annually re-weighted chain volume indexes are referenced to the current price values in a chosen reference year. Reference: Australian National Accounts: State Accounts (cat. no. 5220.0).
Civilian population aged 15 years and over
All usual residents of Australia aged 15 years and over except members of the permanent defence forces, certain diplomatic personnel of overseas governments customarily excluded from census and estimated population counts, overseas residents in Australia, and members of non-Australian defence forces (and their dependants) stationed in Australia. Reference: Labour Force, Australia (cat. no. 6202.0).
Closed drug treatment episodes
Refers to a period of contact, with defined dates of commencement and cessation, between a client and a treatment agency. Reference: Alcohol and Other Drug Treatment Services in NSW, Findings from the National Minimum Dataset (AODS-NMDS) October 2004, Australian Institute of Health and Welfare.
Community-based corrections
This refers to the community-based management of court-ordered sanctions, post-prison administrative arrangements and fine conversions, which principally involve the provision of one or more of the following activities: supervision, programs or community work. Reference: Corrective Services, Australia (cat. no. 4512.0).
Community Aged Care Packages
A Commonwealth-funded program designed to provide assistance to enable frail or disabled older people with complex care needs to continue living in the community. Reference: Residential Aged Care in Australia, 2004, Australian Institute of Health and Welfare.
Community health
Non-residential health services offered by public or registered non-profit establishments to patients/clients, in an integrated and coordinated manner in a community setting, or the coordination of health services elsewhere in the community. Reference: Health Expenditure Australia 2002-03, Australian Institute of Health and Welfare.
Community Service Order
The offender is ordered to perform a specified number of hours of unpaid community service work.
Reference: NSW Criminal Courts Statistics 2003, Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research.
Consumption of fixed capital
The reduction in the value of fixed assets used in production during the accounting period resulting from physical deterioration, normal obsolescence or normal accidental damage. Unforeseen obsolescence, major catastrophes and the depletion of natural resources are not taken into account. Reference: Australian National Accounts: State Accounts (cat. no. 5220.0).
Control order
Includes fixed term, minimum and additional term with Department of Juvenile Justice supervision, minimum and additional term with other supervision and minimum and additional term with no supervision. Reference: NSW Criminal Courts Statistics 2003, Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research.
Convicted ex parte
Includes cases where the accused either: (i) pleaded guilty and was convicted in his/her absence; or (ii) failed to appear, was convicted by the court on the evidence presented and a conviction warrant issued by the court for the offender in order to impose a penalty. Reference: NSW Criminal Courts Statistics 2003, Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research.
Core activity limitation
A person's overall level of core activity limitation is determined by their highest level of limitation in any of the core activities (communication, mobility or self care). There are four levels:
- profound: the person is unable to do, or always needs help with, a core-activity task
- severe: the person sometimes needs help with a core-activity task; or has difficulty understanding or being understood by family or friends; or can communicate more easily using non-spoken forms of communication
- moderate: the person needs no help but has difficulty with a core activity task
- mild: the person needs no help and has no difficulty with any of the core activity tasks, but uses aids and equipment; or cannot easily walk 200 metres or up and down stairs without a handrail or easily bend to pick up an object from the floor or has difficulty using public transport.
Reference: Disability, Ageing and Carers, Australia (cat. no. 4430.0).
Couple family
A family based on two persons who are in a registered or de facto marriage and who are usually resident in the same household. The family may include any number of dependents, non-dependants and other related individuals. A couple family can consist of a couple without children present in the household. Reference: Family Characteristics, Australia (cat. no. 4442.0).
Crude divorce rate
The number of decrees absolute granted during the calendar year, per 1,000 estimated resident population at 30 June. Reference: Divorces, Australia (cat. no. 3307.0.55.001).
Crude marriage rate
The number of marriages registered during the calendar year, per 1,000 estimated resident population at 30 June. Reference: Marriages, Australia (cat. no. 3306.0.55.001).
Current prices
Estimates are valued at the prices of the period to which the observation relates. For example, estimates for 2003-04 are valued using 2003-04 prices. This contrasts to chain volume measures where the prices used in valuation refer to the prices of a previous period. Reference: Australian National Accounts: State Accounts (cat. no. 5220.0).
De facto marriage
The relationship between two people who live together in a consensual union who are not registered as married to each other. A de facto marriage may exist between a couple of the opposite sex or of the same sex. Reference: Family Characteristics, Australia (cat. no. 4442.0).
Death
For the purposes of the Vitals and Causes of Death collections of the ABS, a death refers to any death which occurs in, or en route to Australia and is registered with a state or territory Registry of Births, Deaths and Marriages. Reference: Deaths, Australia (cat. no. 3302.0).
Dependent child
An individual who is either a child aged under 15 years or a child aged 15-24 years who is a full-time dependent student. To be regarded as a child the individual cannot have a partner or child of his or her own usually resident in the household. Reference: Family Characteristics, Australia (cat. no. 4442.0).
Disability
A limitation, restriction or impairment which has lasted, or is likely to last, for at least six months and restricts everyday activities. Reference: Disability, Ageing and Carers, Australia (cat. no. 4430.0).
Disposable income
Gross income after income tax and the Medicare levy are deducted and family tax benefit paid through the tax system or as a lump sum by Centrelink is added. Disposable income is sometimes referred to as net income. Reference: Household Income and Income Distribution, Australia (cat. no. 6523.0).
Drug-induced deaths
Any death where the underlying cause of death was due to:
- An acute episode of poisoning or toxicity to drugs. Included are deaths from accidental overdoses due to misuse of drugs, intentional self-harm, assault and deaths undetermined as to intent.
- An acute condition caused by drug use where the deceased person was identified as drug dependent.
The term 'drug' refers to substances classified as drugs, medicaments or biological substances under ICD-10 guidelines. These drugs may by used for medicinal or therapeutic purposes, or to produce a psychoactive effect. The term excludes alcohol, tobacco and volatile solvents (e.g. petrol). Reference: Information paper: Drug-Induced Deaths - A Guide to ABS Causes of Death Data (cat. no. 4809.055.001).
Duration of imprisonment
Average duration of imprisonment is the mean length of time in months of the non-parole period imposed on the principal offence. As imprisonment is the most serious penalty which can be imposed, the data includes all charges where an imprisonment penalty was imposed. Sentences of cumulative imprisonment are excluded, in which case, only the penalty for the principal offence is shown. The calculation of the average duration of imprisonment does not include sentences of life imprisonment. Reference: NSW Criminal Courts Statistics 2003, Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research.
Employed
All persons aged 15 years and over who, during the reference week:
- worked for one hour or more for pay, profit, commission or payment in kind, in a job or business, or on a farm (comprising employees, employers and own account workers); or
- worked for one hour or more without pay in a family business or on a farm (i.e. contributing family workers); or
- were employees who had a job but were not at work; or
- were employers or own account workers, who had a job, business or farm but were not at work.
Reference: Australian Labour Market Statistics (cat. no. 6105.0).
Employment restriction
An employment restriction is determined for persons with one or more disabilities if because of their disability they are: permanently unable to work; or are restricted in the type of work they can do; or need at least one day a week off work on average, or are restricted in the number of hours they can work; or require an employer to provide special equipment, or modify the work environment, or make special arrangements; or need to be given ongoing assistance or supervision; or require assistance from a disability job placement program; or would find it difficult to change jobs or get a preferred job. Reference: Disability, Ageing and Carers, Australia (cat. no. 4430.0).
Endangered ecological communities
An ecological community is eligible to be listed as an endangered ecological community if, in the opinion of the Scientific Committee:
(a) it is likely to become extinct in nature in NSW unless the circumstances and factors threatening its survival cease to operate, or;
(b) it might already be extinct.
Reference: Threatened Species Conservation Act 1995.
Endangered species
A species is eligible to be listed as an endangered species if, in the opinion of the Scientific Committee:
(a) it is likely to become extinct in nature in NSW unless the circumstances and factors threatening its survival or evolutionary development cease to operate, or;
(b) its numbers have been reduced to such a critical level, or its habitats have been so drastically reduced, that it is in immediate danger of extinction, or;
(c) it might already be extinct, but is not presumed extinct.
Reference: Threatened Species Conservation Act 1995.
Endangered populations
A population is eligible to be listed as an endangered population if, in the opinion of the Scientific Committee, it is facing a high risk of becoming extinct in nature in NSW and it is of conservation value at the State or regional level. The intention of the criteria is to exclude from listing isolated populations of limited conservation value. Reference: Threatened Species Conservation Act 1995.
Equivalised disposable household income
Disposable household income adjusted using an equivalence scale. For a lone person household it is equal to disposable household income. For a household comprising more than one person, it is an indicator of the disposable household income that would need to be received by a lone person household to enjoy the same level of economic well-being as the household in question. Reference: Household Income and Income Distribution, Australia (cat. no. 6523.0).
Established dwelling
Is a dwelling that has been completed for 12 months or more prior to the lodgement of a loan application, or has been previously occupied. Reference: Lending Finance, Australia (cat. no. 5671.0).
Estimated Resident Population (ERP)
The official measure of the population of Australia is based on the concept of residence. It refers to all people, regardless of nationality or citizenship, who usually live in Australia, with the exception of foreign diplomatic personnel and their families. It includes usual residents who are overseas for less than 12 months. It excludes overseas visitors who are in Australia for less than 12 months. Reference: Australian Demographic Statistics (cat. no. 3101.0).
Exercise level
Based on frequency, intensity (i.e. walking, moderate exercise and vigorous exercise) and duration of exercise (for recreation, sport or fitness) in the two weeks prior to interview. From these components, an exercise score was derived using factors to represent the intensity of the exercise. Scores were grouped for output as Sedentary (includes no exercise), Low, Moderate, or High. Reference: ABS National Health Survey: Summary of Results, 2001 (cat. no. 4364.0).
Family
Two or more persons, one of whom is at least 15 years of age, who are related by blood, marriage (registered or de facto), adoption, step or fostering; and who are usually resident in the same household. The basis of a family is formed by identifying the presence of a couple relationship, lone parent-child relationship or other blood relationship. Some households will, therefore, contain more than one family. Reference: Family Characteristics, Australia (cat. no. 4442.0).
Family day care
A type of formal care offered in private homes by registered carers, available for a full day or part day to children of all ages. Reference: Child Care, Australia (cat. no. 4402.0).
Fetal death
A fetal death is the delivery of a child, who did not, at any time after delivery, breathe or show any other evidence of life such as a heartbeat. A birthweight criterion applies (see perinatal death). Reference: Causes of Death, Australia (cat. no. 3303.0).
Final consumption expenditure (general government)
Net expenditure on goods and services by public authorities, other than those classified as public corporations, which does not result in the creation of fixed assets or inventories or in the acquisition of land and existing buildings or second-hand assets. Reference: Australian National Accounts: State Accounts (cat. no. 5220.0).
Final consumption expenditure (households)
Net expenditure on goods and services by persons and expenditure of a current nature by private non-profit institutions serving households. This item excludes expenditures by unincorporated businesses and expenditures on assets by non-profit institutions (included in gross fixed capital formation). Reference: Australian National Accounts: State Accounts (cat. no. 5220.0).
Finance commitment
A firm offer of finance which either has been, or is normally expected to be, accepted. Commitments accepted and cancelled in the same month are included. Commitments to non-residents are excluded.
Reference: Lending Finance, Australia (cat. no. 5671.0).
Finance lease
Refers to the leasing or hiring of tangible assets under an agreement, other than a hire purchase agreement, which substantially transfers from the lessor to the lessee all the risks and benefits incident to ownership of the asset without transferring the legal ownership. Reference: Lending Finance, Australia (cat. no. 5671.0).
Fixed loans
A commitment for a fixed amount for a fixed period for a specific purpose. Reference: Lending Finance, Australia (cat. no. 5671.0).
Forestry reserve
Public lands managed and controlled by state or territory forestry services in accordance with forestry acts and regulations. Reference: National Public and Aboriginal Lands (NPAL) Database, Geoscience Australia.
Formal child care
Regulated care away from the child's home. Reference: Child Care, Australia (cat. no. 4402.0).
Formal reserves
Nature conservation reserves and reserves meeting the International Union for the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) categories as defined by the IUCN Commission for National Parks and Protected Areas (1994). Reference: Australia's State of the Forests Report, 2003, Bureau of Rural Sciences.
Free-standing day hospital facilities
These provide investigation and treatment for acute conditions on a day-only basis and are approved by the Commonwealth for the purposes of basic table health insurance benefits. Reference: Private Hospitals Australia (cat. no. 4390.0).
Fugitive emissions
These emissions are not fully controlled, but in most cases are not accidental. Examples of fugitive emissions are leaks from gas pipelines and valves, venting and flaring of gases, methane emissions from coal seams and vapour given off by petroleum stores. Reference: The National Greenhouse Strategy, 1998, NSW Department of Environment and Heritage.
Full-time equivalent (FTE)
A measure of the total level of staff resources used. The FTE of a full-time staff member is equal to 1.0. The calculation of FTE for part-time staff is based on the proportion of time worked compared with that worked by full-time staff performing similar duties. Casual staff are excluded. Reference: Schools, Australia (cat. no. 4221.0).
Greenhouse gas
Gases that contribute to global warming, including carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), and sulphur hexafluoride (SF6). In addition, the photochemically important gases-NMVOCs, oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and carbon monoxide (CO)-are also considered. NMVOC, NOx and CO are not direct greenhouse gases. However, they contribute indirectly to the greenhouse effect by influencing the rate at which ozone and other greenhouse gases are produced and destroyed in the atmosphere. Reference: Nationals Greenhouse Gas Inventory, 2002, NSW Department of Environment and Heritage.
Government income support
The data have been compiled using Centrelink data on income support customers. People receiving more than one Department of Family and Community Services payment are only counted once by using the main payment type. The main payments types include: Age pension; Disability Support Pension; Newstart Allowance; Parenting Payment Single; Youth Allowance; and other pensions and allowances. Excluded are Bereavement Allowance, Childcare Benefit, Farm Family Restart, and Family Tax Benefits Parts A and B. The data includes both customers receiving a payment and those customers temporarily suspended or zero paid due to income/assets test provisions or other administrative procedures. Reference: Department of Family and Community Services.
Government pensions and allowances/Government cash benefits
Regular, recurring receipts from government to persons under social security and related government programs. Included are pensions and allowances received by aged, disabled, unemployed and sick persons, families and children, veterans or their survivors, and study allowances for students. All overseas pensions and benefits are included here, although some may not be paid by overseas governments. Reference: Household Income and Income Distribution, Australia (cat. no. 6523.0).
Greater Metropolitan Area (GMA)
The Transport and Population Data Centre (TPDC) defined area for core TPDC data sets. Comprises Sydney SD, Newcastle SSD and Illawarra SD. Reference: 2002 Household Travel Survey Summary Report, Transport and Population Data Centre, Department of Infrastructure, Planning and Natural Resources.
Gross domestic product (GDP)
The total market value of goods and services produced in Australia within a given period after deducting the cost of goods and services used up in the process of production but before deducting allowances for the consumption of fixed capital. Thus GDP, as here defined, is 'at market prices'. It is equivalent to gross national expenditure plus exports of goods and services less imports of goods and services. Reference: Australian National Accounts: State Accounts (cat. no. 5220.0).
Gross income
Regular cash receipts before income tax or the Medicare levy are deducted. Excludes family tax benefit paid through the tax system or as a lump sum by Centrelink. Reference: Household Income and Income Distribution, Australia (cat. no. 6523.0).
Gross State Product (GSP)
GSP is defined equivalently to gross domestic product (GDP) but refers to production within a state or territory rather than to the nation as a whole. Reference: Australian National Accounts: State Accounts (cat. no. 5220.0).
Gross value of commodities produced
The value placed on commodities at the point of sale (i.e. market place). Reference: Value of Agricultural Commodities Produced (cat. no. 7503.0).
Group household
A household consisting of two or more unrelated people where all persons are aged 15 years or over. There are no reported couple relationships, parent-child relationships or other
blood relationships in these households. Reference: 2001 Census Dictionary (cat. no. 2901.0).
Health professional
Includes health professionals, other than medically qualified doctors, that might be consulted for health problems within the respondent's cultural framework. Reference: National Survey of Mental Health and Wellbeing of Adults: Users' Guide (cat. no. 4327.0).
High-level residential care
Care provided to residents in residential care facilities who have been classified as having a need for and are receiving a very high level of care (i.e. patients classified in RCS categories 1-4). Reference: Health Expenditure Australia 2002-03, Australian Institute of Health and Welfare.
Higher court
There are two jurisdictions in the NSW Higher Courts, the Supreme Court which hears cases in Sydney and on circuit in country centres periodically, and the District Court which has a number of metropolitan and country sites. The Supreme Court deals only with the most serious matters. The District Court deals with all other matters on indictment and appeals against conviction or sentence arising from Local Court cases.
Reference: NSW Criminal Courts Statistics 2003, Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research.
Home detention
An alternative means of serving sentences of full-time imprisonment of up to 18 months. The conditions of the Order constrain the offender‘s liberty to an extent that approximates confinement in minimum security custody with access to day release programs. Reference: NSW Criminal Courts Statistics 2003, Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research.
Higher education student
A person who has been admitted to a higher education institution and who is enrolled (either full-time, part-time or externally) in a higher education award course, an enabling course or a non-award course to be undertaken in the semester used as the reference period. Reference: Students 2003: Selected Higher Education Statistics, Department of Education Science and Training.
Homelessness
Includes 'primary', 'secondary' and 'tertiary' homelessness. Primary homelessness: people without conventional accommodation (living on the streets, in deserted buildings, improvised dwellings, under bridges, in parks etc.). Secondary homelessness: people moving between various forms of temporary shelter including friends, emergency accommodation, youth refuges, hostels and boarding houses. Tertiary homelessness: people living in single rooms in private boarding houses - without their own bathroom, kitchen, or security of tenure. Reference: Counting the Homeless (cat. no. 2050.0).
Hospital separations
The formal process whereby an inpatient leaves a hospital or other area health service facility after completing an episode of care. For example, a discharge to home, discharge to another hospital or nursing home, or death. Reference: The Health of the people of New South Wales - Report of the Chief Health Officer, NSW Department of Health.
House price index
The Established House Price index refers to detached residential dwellings on their own block of land regardless of age. Price changes therefore relate to changes in the total price of dwelling and land. The Project Home Price index refers to dwellings available for construction on a client's block of land. Price therefore relate only to the price of the dwelling (excluding land). Reference: House Price Indexes: Eight Capital Cities (cat. no. 6416.0).
Household
A group of two or more related or unrelated people who usually reside in the same dwelling, who regard themselves as a household, and who make common provision for food or other essentials for living; or a person living in a dwelling who makes provision for his/her own food and other essentials for living, without combining with any other person. Reference: Family Characteristics, Australia (cat. no. 4442.0).
Back to Top
Imprisonment
An order requiring a person to be detained within a facility built especially for the purpose of incarceration. Includes: Life and indeterminate imprisonment, Imprisonment with determined term and Periodic detention.
Reference: Criminal Courts, Australia (cat. no. 4513.0).
In-stream water use
The use of freshwater in situ, such as water use for hydro-electricity generation and aquaculture purposes is classified as in-stream use, and is included in the accounts as self-extracted water use. In-stream volumes are considered to be a type of non-consumptive use, for although these volumes are also considered to be a form of regulated discharge, an economic benefit is gained from the use of the water prior to discharge.
Reference: Water Account, Australia (cat. no. 4610.0).
Indirect standardised death rate
Standardised death rates enable the comparison of death rates between populations with different age structures by relating them to a standard population. The current standard population is all persons in the 2001 Australian population. The indirect method of standardisation is used when the populations under study are small and the age-specific death rates are unreliable or not known. It is an adjustment to the crude death rate of the standard population to account for the variation between the actual number of deaths in the population under study and the number of deaths which would have occurred if the population under study had experienced the age-specific death rates of the standard population. Reference: Deaths, Australia (cat. no. 3302.0).
Industry value added (IVA)
Represents the value added by an industry to the intermediate inputs used by the industry. IVA is the measure of the contribution by businesses, in the selected industry, to gross domestic product. Reference: Australian Industry (cat. no. 8155.0).
Infant death
An infant death is the death of a live-born child who dies before completing his or her first birthday.
Reference: Deaths, Australia (cat. no. 3302.0).
Infant mortality rate
The number of deaths of children under one year of age in a calendar year per 1,000 live births in the same calendar year. Reference: Deaths, Australia (cat. no. 3302.0).
Informal child care
Non-regulated care, arranged by a child's parent/guardian, either in the child's home or elsewhere. It may be paid or unpaid. Reference: Child Care, Australia (cat. no. 4402.0).
Informal reserve
An area reserved on non-nature conservation reserve tenure through both legislated and non-legislated means. The status of informal reserves is not secure, relying on the state or territory management agency responsible for the interpretation and application of the guidelines applicable to the area within an informal reserve. Reference: Australia's State of the Forests Report, 2003, Bureau of Rural Sciences.
Injured
A person who is injured as a result of a crash, and who does not die as a result of those injuries within 30 days of the crash. Reference: Road Traffic Accidents, 2003, Roads and Traffic Authority of NSW.
Intact family
A couple family containing at least one child aged 0-17 years who is the natural or adopted child of both members of the couple, and no child aged 0-17 years who is the step child of either member of the couple. Intact families may also include other children who are not the natural child of either parent. Reference: Family Characteristics, Australia (cat. no. 4442.0).
Back to Top
Killed
A person who dies within 30 days of a crash as a result of injuries received in that crash. Reference: 2002 Household Travel Survey Summary Report, Transport and Population Data Centre, Department of Infrastructure, Planning and Natural Resources.
Labour force
For any group, persons who were employed or unemployed, as defined. Reference: Labour Force, Australia (cat. no. 6202.0).
Labour price index
Measures changes in the price of labour. Includes wages and salaries, overtime, bonuses (only in the labour price including bonuses index), annual and public holiday leave, superannuation, payroll tax and workers' compensation. Reference: Labour Price Index, Australia (cat. no. 6345.0).
Land showing signs of salinity
Land with dead trees, salt scalds or salt tolerant plants (e.g. sea barley grass, red weed, beadbush and samphire), land where crops and pastures are unable to be grown and land that is waterlogged for significant parts of the year. Reference: Salinity on Australian Farms (cat. no. 4615.0).
Landlord type
Renters belong to one of the following categories:
- state or territory housing authority: where the household pays rent to a State or Territory housing authority or trust
- private landlords: where the household pays rent to a real estate agent or to another person not in the same household
- other: where the household pays rent to the owner/manager of a caravan park, an employer (including a government authority), a housing cooperative, a community or church group, or any other body not included elsewhere.
Reference: Household Income and Income Distribution, Australia (cat. no. 6523.0).
Life expectancy
Life expectancy refers to the average number of additional years a person of a given age and sex might expect to live if the age-specific death rates of the given period continued throughout his or her lifetime.
Reference: Deaths, Australia (cat. no. 3302.0).
Linked trip
A linked trip is a journey from one activity to another, ignoring changes of modes. A linked trip comprises one or more unlinked trip legs. For example, a person who lives in Parramatta may travel to work in Sydney Central Business District by train with a walk trip to and from the train. This would be counted as one linked trip from home to work. Reference: 2002 Household Travel Survey Summary Report, Transport and Population Data Centre, Department of Infrastructure, Planning and Natural Resources.
Literacy national benchmarks
The benchmarks that underpin the reporting of student achievement describe nationally agreed minimum acceptable standards for aspects of literacy i.e. reading and writing at particular year levels. That is, they represent the minimum acceptable standard without which a student will have difficulty making sufficient progress at school. Reference: National Report on Schooling in Australia, Ministerial Council on Education, Employment, Training and Youth Affairs.
Livestock slaughterings and other disposals
Values are published as one figure but include two distinct components: value of livestock slaughtered and value of net exports. Reference: Value of Agricultural Commodities Produced (cat. no. 7503.0).
Local court
A Lower Court level (also referred to as Magistrates' Court, Local Court or Court of Petty Sessions) which deals with relatively less serious charges and has the most limited legal powers of all the state and territory court levels. A Court of Summary Jurisdiction is presided over by a Magistrate and has jurisdiction to try and sentence matters relating to summary offences. Under some circumstances, this court level may also deal with less serious indictable offences known as 'minor indictable' or 'triable either way' offences. Courts of Summary Jurisdiction are also responsible for conducting preliminary (committal) hearings for indictable offences. Reference: NSW Criminal Courts Statistics 2003, Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research.
Lone person
A person who makes provision for his or her own food and other essentials for living, without combining with any other person to form part of a multi-person household. He or she may live in a dwelling on their own or share a dwelling with another individual or family. Reference: Family Characteristics, Australia (cat. no. 4442.0); 2001 Census Dictionary (cat. no. 2901.0).
Long-term arrival and departures
Long-term arrivals comprise overseas visitors who intend to stay in Australia for 12 months or more (but not permanently) and Australian residents returning after an absence of 12 months or more overseas. Long-term departures comprise Australian residents who intend to stay abroad for 12 months or more (but not permanently) and overseas visitors departing who stayed 12 months or more in Australia. Reference: Overseas Arrival and Departures (cat. no. 3401.0).
Long-term health condition
A disease or disorder which has lasted or is likely to last for at least six months; or a disease, disorder or event (e.g. stroke, poisoning, accident etc.) which produces an impairment or restriction which has lasted or is likely to last for at least six months. Reference: Disability, Ageing and Carers, Australia (cat. no. 4430.0).
Marginally housed
People in housing situations close to the minimum standard. Reference: Counting the Homeless (cat. no. 2050.0).
Marine reserve
Crown marine environments managed by state or territory or the Australian Government, reserved for the preservation of flora and fauna. Reference: National Public and Aboriginal Lands (NPAL) Database, Geoscience Australia.
Mean income
The total income received by a group of units divided by the number of units in the group. Reference: Household Income and Income Distribution, Australia (cat. no. 6523.0).
Median income
That level of income which divides the units in a group into two equal parts, one half having incomes above the median and the other half having incomes below the median. Reference: Household Income and Income Distribution, Australia (cat. no. 6523.0).
Mental disorder
According to the ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders, a disorder implies 'the existence of a clinically recognisable set of symptoms or behaviour associated in most cases with distress and with interference with personal functions' (WHO 1992, p. 5). Most diagnoses require criteria relating to severity and duration to be met. Reference: National Survey of Mental Health and Wellbeing of Adults: Users' Guide (cat. no. 4327.0).
Migration adjustment
The ABS applies a number of adjustments to overseas arrivals and departures data in order to produce estimates of net overseas arrivals and departures (NOM). These mainly comprise adjustments designed to reflect differences between stated travel intentions and actual travel behaviour, but (in the case of revised NOM estimates) also include adjustments to transform numbers of overseas movements into numbers of travellers. Reference: Australian Demographic Statistics (cat. no. 3101.0).
Mining reserve
Crown lands held in reserves for mining. Reference: National Public and Aboriginal Lands (NPAL) Database, Geoscience Australia.
Mode of travel
Unlinked trips have only one mode and one purpose. Linked trips can comprise more than one mode so a priority mode is allocated to each trip based on a determined priority of modes. Reference: 2002 Household Travel Survey Summary Report, Transport and Population Data Centre, Department of Infrastructure, Planning and Natural Resources.
Multiple-use forest
State forest, timber reserves and other forest areas on which a range of forest values are managed including timber harvesting, water supply, conservation of biodiversity, recreation and environmental protection. They are managed by state or territory agencies in accordance with relevant Acts and regulations. Reference: Australia's State of the Forests Report, 2003, Bureau of Rural Sciences.
Natural increase
Excess of births over deaths. Reference: Australian Demographic Statistics (cat. no. 3101.0).
Nature conservation reserves
Includes national parks, nature reserves, state or territory recreation areas, conservation parks, environmental parks etc. These are Crown lands reserved for specific environmental conservation purposes such as protection of wildlife, protection of a type of habitat or preservation of an area with natural features of scientific or recreational value. National parks are generally large areas of scenic or other natural significance to the general public. Reference: National Public and Aboriginal Lands (NPAL) Database, Geoscience Australia.
Net capital expenditure
The value of total capital expenditure less proceeds received from the disposal of fixed tangible assets.
Reference: Electricity, Gas, Water and Sewerage Operations, Australia (cat. no. 8226.0).
Net interstate migration
The difference between the number of persons who have changed their place of usual residence by moving into a given state or territory and the number who have changed their place of usual residence by moving out of that state or territory during a specified time period. This difference can be either positive or negative.
Reference: Australian Demographic Statistics (cat. no. 3101.0).
Net overseas migration
Net overseas migration is net permanent and long-term overseas migration, adjusted for change in traveller duration, intention and multiple movement error. Reference: Australian Demographic Statistics (cat. no. 3101.0).
Neonatal death
A neonatal death is the death within 28 days of any child who, after delivery breathed or showed any other evidence of life such as a heartbeat. A birthweight criterion applies (see perinatal death). Reference: Causes of Death, Australia (cat. no. 3303.0).
New dwelling
Is a dwelling that has been completed within 12 months of the lodgement of a loan application, and the borrower will be the first occupant. Reference: Housing Finance, Australia (cat. no. 5609.0).
Non-private dwelling
Dwellings that provide a communal or transitory type of accommodation. They include hotels, motels, guest houses, prisons, religious and charitable institutions, defence establishments, hospitals and other communal dwellings. Reference: 2001 Census Dictionary (cat. no. 2901.0).
Non-school qualification
Non-school qualifications are awarded for educational attainments other than those of pre-primary, primary or secondary education. They include qualifications at the Post Graduate Degree level, Master Degree level, Graduate Diploma and Graduate Certificate level, Bachelor Degree level, Advanced Diploma and Diploma level, and Certificates I, II, III and IV levels. Reference: Education and Work, Australia (cat. no. 6227.0).
Notifiable disease
Certification in an approved form of a disease listed in the Schedule 3 of Notifiable Diseases of the NSW Public Health Act 1991. Reference: The Health of the people of New South Wales - Report of the Chief Health Officer, NSW Department of Health.
Numeracy national benchmarks
The benchmarks that underpin the reporting of student achievement describe nationally agreed minimum acceptable standards for aspects of numeracy at grades 3, 5 and 7. They represent the minimum acceptable standard without which a student will have difficulty making sufficient progress at school. Reference: National Report on Schooling in Australia, Ministerial Council on Education, Employment, Training and Youth Affairs.
Back to Top
Occupational diseases
Includes diseases contracted or aggravated in the course of employment and to which employment was a contributing factor. Reference: Workers Compensation Statistics, 1999-2000 to 2002-03, WorkCover NSW.
Offence proven (Children's Court)
Proven offences include those appearances resulting in referral to drug programs, return to former custody, revoked or amended community service orders and referrals to other jurisdictions. Appearances resulting in Apprehended Violence Orders are not included. Reference: NSW Criminal Courts Statistics 2003, Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research.
One parent family
A family consisting of a lone parent with at least one dependent or non-dependant child (regardless of age) who is also usually residing in the household. Reference: Family Characteristics, Australia (cat. no. 4442.0).
Operating profit before tax (OPBT)
Profit before extraordinary items are brought to account and prior to the deduction of income tax and appropriations to owners (e.g. dividends paid), i.e. total income - total expenses + change in inventories.
Reference: Australian Industry (cat. no. 8155.0).
Other health professional (OHP)
Comprises: Aboriginal health worker (n.e.c.), Accredited counsellor, Acupuncturist, Alcohol and drug worker (n.e.c.), Audiologist/Audiometrist, Chemist (for advice), Chiropodist/podiatrist, Chiropractor, Dietitian/Nutritionist, Herbalist, Hypnotherapist, Naturopath, Nurse, Occupational therapist, Optician/optometrist, Osteopath, Physiotherapist/hydrotherapist, Psychologist, Social worker/welfare officer, Speech therapist/pathologist. Reference: National Health Survey: Summary of Results (cat. no. 4364.0).
Other income
Income other than wages and salaries, own business or partnership income and government pensions and allowances. This includes income received as a result of ownership of financial assets (interest, dividends), and of non-financial assets (rent, royalties) and other regular receipts from sources such as superannuation, child support, workers' compensation and scholarships. Income from rent is net of operating expenses and depreciation and may be negative when these are greater than gross receipts. Reference: Household Income and Income Distribution, Australia (cat. no. 6523.0).
Overseas arrivals and departures (OAD)
Refers to the arrival or departure of persons, through Australian airports (or sea ports), which have been recorded. Statistics on OAD relate to the number of movements of travellers rather than the number of travellers (i.e. the multiple movements of individual persons during a given reference period are all counted).
Reference: Overseas Arrival and Departures (cat. no. 3401.0).
Overweight or obese adults
Overweight is defined by a body mass index (BMI) greater than or equal to 25 and less than 30, while obesity is defined by a BMI greater than or equal to 30. BMI is body weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in metres. Reference: National Health Survey: Summary of Results (cat. no. 4364.0).
Own unincorporated business income
The profit/loss that accrues to persons as owners of, or partners in, unincorporated enterprises. Profit/loss consists of the value of gross output of the enterprise after the deduction of operating expenses (including depreciation). Losses occur when operating expenses are greater than gross receipts and are treated as negative income. Reference: Household Income and Income Distribution, Australia (cat. no. 6523.0).
Participation rate
For any group, the labour force expressed as a percentage of the civilian population aged 15 years and over in the same group. Reference: Labour Force, Australia (cat. no. 6202.0).
Patient days
These are the aggregate number of days of stay (i.e separation date minus admission date) for all overnight-stay patients who were separated from hospital during the year. Periods of approved leave are subtracted from these calculations. Same-day patients are each counted as having a stay of one day.
Reference: Private Hospitals, Australia (cat. no. 4390.0).
Perinatal death
A perinatal death is a fetal death or neonatal death. Perinatal death statistics include all fetuses and infants delivered weighing at least 400 grams or (when birthweight is unavailable) the corresponding gestational age (20 weeks), whether alive or dead. Period of gestation is measured from the first day of the last normal menstrual period to the date of birth and is expressed in completed weeks. Reference: Causes of Death, Australia (cat. no. 3303.0).
Periodic detention
The offender is held in custody in prison periodically (at weekends for example) for a specified period.
Reference: NSW Criminal Courts Statistics 2003, Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research.
Permanent arrival and departures
Permanent arrivals comprise travellers who hold migrant visas and other persons eligible to settle, and permanent departures comprise Australian residents who intend to settle in another country. Reference: Overseas Arrival and Departures (cat. no. 3401.0).
Persons charged
A person charged refers to a group of one or more charges, against a single individual, which are finalised by the court on a single day. Such a group of finalised charges against a single individual is also referred to as a finalised court appearance (A company charged with an offence is treated as a person). If a person is a defendant in more than one court appearance during the counting period, such a person will be counted more than once in the report. Reference: NSW Criminal Courts Statistics 2003, Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research.
Person of interest (POI)
The person who is reported and/or identified as involved in a criminal incident. A POI may become an offender if charged, may be found not to be involved in the incident, or the allegation may be with withdrawn. A single POI can be linked to one or more offences. POIs can also be involved in more than one incident in any reference period. Reference: Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research; NSW Police.
Population growth
For Australia, population growth is the sum of natural increase and net overseas migration. For states and territories, population growth also includes net interstate migration. After the Census, intercensal population growth also includes an allowance for intercensal discrepancy. Reference: Australian Demographic Statistics (cat. no. 3101.0).
Population projections
The ABS produces several series of population projections based on different combinations of assumptions about mortality, fertility and migration. The assumptions underlying series B most closely reflect prevailing trends and comprise: declining rates of mortality; the total fertility rate for Australia falling to 1.6 by 2001, and then remaining constant; low levels of overseas migration (Australian annual net gain of 100,000 from 2005-06); and medium levels of interstate migration. Reference: Population Projections, Australia (cat. no. 3222.0).
Presumed extinct (species)
A species is eligible to be listed as a species that is presumed extinct at a particular time if, in the opinion of the Scientific Committee, it has not been recorded in its known or expected habitat in NSW, despite targeted surveys, over a time frame appropriate, in the opinion of the Scientific Committee, to its life cycle and form.
Reference: Threatened Species Conservation Act 1995.
Principal source of income
That source from which the most positive income is received. If total income is nil or negative the principal source is undefined. Reference: Household Income and Income Distribution, Australia (cat. no. 6523.0).
Priority purpose
Return to home trips are coded according to the main previous purpose. For example, if a person is returning home from work and stopped off at the shops quickly on the way, the incidental trip is ignored and the main purpose remains 'work'. Reference: 2002 Household Travel Survey Summary Report, Transport and Population Data Centre, Department of Infrastructure, Planning and Natural Resources.
Private dwelling
Normally a house, flat or even a room. It can also be a caravan, houseboat, tent, or a house attached to an office or rooms above a shop. Reference: 2001 Census Dictionary (cat. no. 2901.0).
Private health insurance
Provides cover against all or part of hospital theatre and accommodation costs in either a public or private hospital, medical costs in hospital, and costs associated with a range of services, not covered under Medicare including private dental services, optical, chiropractic, home nursing, ambulance, natural therapies and other ancillary services. Ancillary insurance covers services such as dental, optical, therapies and other general non-accommodation services. Reference: Private Health Insurance Administration Council.
Private new capital expenditure
Refers to the acquisition of new tangible assets either on own account or under a finance lease and includes major improvements, alterations and additions. In general, this is expenditure charged to fixed tangible assets accounts excluding expenditure on second hand assets unless these are imported for the first time.
Reference: Private New Capital Expenditure and Expected Expenditure, Australia (cat. no. 5625.0).
Proficiency in spoken English
An indicator of a person's ability to speak English and not a definitive measure of his or her ability.
Reference: 2001 Census Dictionary (cat. no. 2901.0).
Qualification
Formal certification, issued by a relevant approved body, in recognition that a person has achieved learning outcomes or competencies relevant to identified individual, professional, industry or community needs. Statements of attainment awarded for partial completion of a course of study at a particular level are excluded. Reference: Education and Work, Australia (cat. no. 6227.0).
Real gross state income
A measure of the real purchasing power of income generated by production within a state or territory. It is calculated by adjusting the chain volume measure of GSP for changes in the terms of trade. Reference: Australian National Accounts: State Accounts (cat. no. 5220.0).
Recorded criminal incidents
A criminal incident is defined as an activity detected by or reported to police which:
- involved the same offender(s);
- involved the same victim(s);
- occurred at the one location;
- occurred during one uninterrupted period of time;
- falls into one offence category;
- falls into one incident type (for example 'actual', attempted', 'conspiracy').
One incident may involve two offenders assaulting the same victim. This would be recorded as one assault incident. Alternatively, suppose a man reports to police that his neighbour demanded money from him, then assaulted him when he did not comply. For such an event, two criminal incidents are recorded because two distinct offence types are involved, even though the same parties were involved at the same time and in the same place. Reference: NSW Recorded Crime Statistics 2003, Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research.
Recorded victims
For murder and manslaughter only, the counting units used are victims. Under the definition of a criminal incident one murder or manslaughter incident could involve two or more persons being killed. Because of the seriousness of these offences and their relatively small numbers, it was considered to be more appropriate to count the number of victims, rather than the number of criminal incidents. Hence, where one murder incident involves a person killing six people, six murder victims are counted. Reference: NSW Recorded Crime Statistics 2003, Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research.
Refinancing
For personal and commercial finance, represents a commitment to refinance an existing loan. For secured housing finance, only those loans where the refinancing lender is not the original lender and the security is unchanged are included. The refinancing of a loan to fund a change of residence is treated as a new lending commitment. Reference: Lending Finance, Australia (cat. no. 5671.0).
Regional Forest Agreements (RFAs)
As a result of the RFAs some areas of forest were assigned formal reserve status for inclusion in the national reserve system. In these cases, the reserved area is assigned ‘pending’ status until the changes are passed through the relevant state or territory parliament, at which time the reserves become legally protected as formal reserves. Other areas are designated informal reserves through zoning regimes in forest management planning process-such as Special Protection Zones - without being established through separate legislation.
Reference: National Public and Aboriginal Lands (NPAL) Database, Geoscience Australia.
Regional Pollution Index (RPI)
The RPI reports are based on measured concentrations of ozone and nitrogen dioxide and a measure of visibility. The RPI is categorised as Low, Medium or High, as follows:
- Low: pollution index from 0 to 24
- Medium: pollution index from 25 to 49
- High: pollution index 50 or higher
When the RPI is reported as High it indicates that the determining pollutant levels have reached or exceeded the relevant standard or goal. Reference: NSW Department of Environment and Conservation.
Retail turnover
Turnover includes retail sales; wholesale sales; takings from repairs, meals and hiring of goods (except for rent, leasing and hiring of land and buildings); commissions from agency activity; and net takings from gaming machines etc. From July 2000, turnover includes the Goods and Service Tax. Reference: Retail Trade, Australia (cat. no. 8501.0).
Residential aged care places
The number of beds which are provided for long-term nursing care to chronically ill, frail or disabled persons, and beds provided for people who are unable to live wholly independently but do not require nursing care, per 1,000 of the population aged 70 years and over. Reference: Residential Aged Care in Australia, 2004, Australian Institute of Health and Welfare.
Re-use (and recycle)
Re-use involves using an item more than once, either for its original purpose or for a different purpose. Examples include re-use of containers (e.g. jars or bottles) for storage, re-use of old clothing for rags, and re-use of plastic bags for shopping or as garbage bags. Reference: Environmental Issues: People's Views and Practices (cat. no. 4602.0).
Revolving credit
A commitment for a credit or borrowing limit is given for a specific period after which the commitment is reviewed. Examples include credit cards, lines of credit and approved overdrafts. Reference: Lending Finance, Australia (cat. no. 5671.0).
Risky/high-risk alcohol status
Males aged 18 years and over who reported drinking more than 50 ml and up to and including 75 ml of absolute alcohol (risky) or more than 75 ml (high-risk) per day, and females aged 18 years and over who reported drinking more than 25 ml and up to and including 50 ml of absolute alcohol (risky) and more than 50 ml (high-risk) on average per day. Reference: National Health Survey: Summary of Results (cat. no. 4364.0).
Road traffic crash
Any apparently unpremeditated event reported to the police and resulted in death, injury or property damage attributable to the movement of a road vehicle on a road. Reference: Road Traffic Accidents, 2003, Roads and Traffic Authority of NSW.
Room occupancy rate
The room occupancy rate represents room occupancy expressed as a percentage of total capacity available during the survey period. Reference: Tourist Accommodation, Australia (cat. no. 8635.0).
Sales and service income
Includes sales of goods, income from services, and rent leasing and hiring. These are valued net of discounts given and exclusive of GST. Extraordinary items are also excluded. Reference: Australian Industry (cat. no. 8155.0).
Schooling restriction
A schooling restriction is determined for persons aged 5-20 years who have one or more disabilities if, because of their disability, they:
- are unable to attend school
- attend a special school
- attend special classes at an ordinary school
- need at least one day a week off school on average
- have difficulty at school.
Reference: Disability, Ageing and Carers, Australia (cat. no. 4430.0).
Socio-Economic Indexes for Areas (SEIFA)-Index of advantage/disadvantage
SEIFA 2001 is a product developed especially for those interested in the assessment of the welfare of Australian communities. The ABS has developed indexes to allow ranking of regions/areas, providing a method of determining the level of social and economic well-being in that region. Low values indicate areas of disadvantage; and high values indicate areas of advantage. A higher score on the Index of Relative Socio-Economic Advantage/Disadvantage indicates that an area has attributes such as a relatively high proportion of people with high incomes or a skilled workforce. It also means an area has a low proportion of people with low incomes and relatively few unskilled people in the workforce. The index scores have been standardised to have a mean of 1,000 and a standard deviation of 100 across all ABS Census Collector Districts (CDs) in Australia. In practice, this means that around 95% of index scores are between 800 and 1,200. SEIFA index scores for CDs have been used to calculate scores for the larger geographic areas by taking the weighted average, using population counts from the 2001 Census, across all CDs which comprised the larger geographic area. Reference: Information Paper: Census of Population and Housing - Socio-Economic Indexes for Areas, Australia (cat. no. 2039.0).
Sex ratio
The sex ratio relates to the number of males per 100 females. Reference: Demography, NSW (cat. no. 3311.1.55.001).
Sexual assault
An incident which was of a sexual nature involving physical contact: includes rape, attempted rape, indecent assault, and assault with intent to sexually assault. Sexual harassment (that did not lead to an assault) was excluded. Only females aged 18 years and over were asked sexual assault questions. Reference: Crime and Safety, NSW (cat. no. 4509.1).
Specific limitation or restriction
A limitation in core activities, or a restriction in schooling and/or employment. Reference: Disability, Ageing and Carers, Australia (cat. no. 4430.0).
State final demand
The aggregate obtained by summing government final consumption expenditure, household final consumption expenditure, private gross fixed capital formation and the gross fixed capital formation of public corporations and general government. It is conceptually equivalent to the Australia level aggregate domestic final demand. Reference: Australian National Accounts: State Accounts (cat. no. 5220.0).
Step family
A couple family containing one or more children aged 0-17 years, none of whom is the natural or adopted child of both members of the couple, and at least on of whom is the step child of either member of the couple. A step family may also include other children who are not the natural children of either parent.
Reference: Family Characteristics, Australia (cat. no. 4442.0).
Student
An individual who was enrolled in a subject or completed a qualification during the reporting period.
Reference: Australian vocational education and training statistics: Students and courses 2003, National Centre for Vocational Education Research.
Supported Accommodation Assistance Program (SAAP)
A joint Commonwealth and State program to assist homeless people and those at risk of homelessness.
Reference: Counting the Homeless (cat. no. 2050.0).
Supported Accommodation Assistance Program (SAAP) client
A person aged 18 years or over, or a person of any age not accompanied by a parent or guardian, who receives support or assistance from a SAAP agency which entails generally one hour or more of a workers' time, either with that client directly or on behalf of that client, on a given day; or is accommodated by a SAAP agency; or enters into an ongoing support relationship with a SAAP agency. Reference: Homeless people in SAAP: SAAP National Data Collection annual report 2002-03 New South Wales supplementary tables, Australian Institute of Health and Welfare
Suspended sentence
A court may impose a sentence of imprisonment of up to two years duration and then suspend the sentence on the condition that the offender enters into a good behaviour bond. Reference: NSW Criminal Courts Statistics 2003, Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research.
Teaching staff
Teaching staff are staff who spend the majority of their time in contact with students. They support students either by direct class contact or on an individual basis, and have teaching duties, that is, are engaged to impart school curriculum. For the purposes of this collection, teaching staff includes principals, deputy principals and senior teachers mainly involved in administration. Teacher aides and assistants, and specialist support staff are excluded. Reference: Schools, Australia (cat. no. 4221.0).
Total expenses
For the purposes of calculating economic and accounting variables, operating expenses incurred by businesses are divided into several categories. Excluded are extraordinary expenses, capitalised expenses, income tax and other direct taxes, GST and excise payable to governments, capital repayments or losses on asset sales, dividends, donations or foreign exchange losses. Reference: Australian Industry (cat. no. 8155.0).
Total factor income
That part of the cost of producing the gross domestic product which consists of gross payments to factors of production (labour and capital). It represents the value added by these factors in the process of production and is equivalent to gross domestic product less taxes plus subsidies on production and imports. Reference: Australian National Accounts: State Accounts (cat. no. 5220.0).
Total fertility rate
The sum of age-specific fertility rates. It represents the number of children a woman would bear during her lifetime if she experienced current age-specific fertility rates at each age of her reproductive life. Reference: Births, Australia (cat. no. 3301.0).
Total hourly rates of pay index
Measures quarterly change in combined ordinary time and overtime hourly rates of pay. Reference: Labour Price Index, Australia (cat. no. 6345.0).
Total income
Comprises sales and service income, interest income and other selected income. Reference: Australian Industry (cat. no. 8155.0).
Underlying cause of death
The disease or injury which initiated the train of morbid events leading directly to death. Accidental and violent deaths are classified according to the external cause, that is, to the circumstances of the accident or violence which produced the fatal injury rather than to the nature of the injury. Reference: Causes of Death, Australia (cat. no. 3303.0).
Unemployed
Persons aged 15 years and over who were not employed during the reference week, and:
- had actively looked for full-time or part-time work at any time in the four weeks up to the end of the reference week and were available for work in the reference week; or
- were waiting to start a new job within four weeks from the end of the reference week and could have started in the reference week if the job had been available then.
Reference: Labour Force, Australia (cat. no. 6202.0).
Unemployment rate
For any group, the number of unemployed persons expressed as a percentage of the labour force in the same group. Reference: Labour Force, Australia (cat. no. 6202.0).
Unlinked trip
An unlinked trip is each component of a linked trip, including each mode used. For example: A person living in Parramatta and working in the Sydney Central Business District travels by train with a walk trip at either end of the train trip. This would be three unlinked trips. Reference: 2002 Household Travel Survey Summary Report, Transport and Population Data Centre, Department of Infrastructure, Planning and Natural Resources.
Unresolved tenure
Areas identified where tenure is unknown or for which there are no data. Most of these are methodological rather than tenure issues. Reference: Australia's State of the Forests Report, 2003, Bureau of Rural Sciences.
Usual daily serves of fruit
A serve of fruit was defined as approximately 150 grams of fresh fruit or 50 grams of dried fruit. Reference: National Health Survey: Summary of Results (cat. no. 4364.0).
Usual daily serves of vegetables
A serve of vegetables was defined as approximately 75 grams of vegetables. Reference: National Health Survey: Summary of Results (cat. no. 4364.0).
Usual residence
Usual residence within Australia refers to that address at which the person has lived or intends to live for a total of six months or more in a given reference year. Reference: Births, Australia (cat. no. 3301.0).
Vacant Crown land
Crown land not reserved for any purpose. Reference: National Public and Aboriginal Lands (NPAL) Database, Geoscience Australia.
Victim (Estimated crime)
A household or person reporting at least one of the offences surveyed. Victims were counted once only for each type of offence, regardless of the number of incidents of that type. Reference: Crime and Safety, NSW (cat. no. 4509.1).
Victimisation rate
The number of victims of an offence in a given population expressed as a percentage of that population.
Reference: Crime and Safety, NSW (cat. no. 4509.1).
Vocational Education and Training (VET) in Schools
A program which allows students to combine vocational studies with their general education curriculum. Students participating in VET in Schools continue to work towards their senior secondary School Certificate, while the VET component of their studies gives them credit towards a nationally recognised VET qualification. VET in Schools programs may involve structured work placements. Reference: Australian vocational education and training statistics: Students and courses 2003, National Centre for Vocational Education Research.
Vocational programs
Type of training programs (as distinct from Non-vocational programs) designed to equip students with vocational skills and knowledge that prepare them for the workplace. This includes general education programs designed for students who may want to undertake vocational programs in the future. Reference: Australian vocational education and training statistics: Students and courses 2003, National Centre for Vocational Education Research.
Vulnerable species
A species is eligible to be listed as a vulnerable species if, in the opinion of the Scientific Committee, the species is likely to become endangered in NSW unless the circumstances and factors threatening its survival or evolutionary development cease to operate. Reference: Threatened Species Conservation Act 1995.
Wages and salaries (Household income and expenditure)
The gross cash income received as a return to labour from an employer or from a person's own incorporated business. Reference: Household Income and Income Distribution, Australia (cat. no. 6523.0).
Wages and salaries (Economic activity)
The gross wages and salaries of all employees of the business. The item includes severance, termination and redundancy payments, salaries and fees, retainers and commissions. Provision expenses for employee entitlements are also included. Payments related to salary sacrifice and payments to self-employed persons are excluded. The drawings of working proprietors and partners are also excluded. Reference: Australian Industry (cat. no. 8155.0).
Wholesale finance
Comprises finance for the purchase of goods by retailers and wholesalers. Reference: Lending Finance, Australia (cat. no. 5671.0).
Wholesale lenders
A wholesale lender provides funds to borrowers through a retail intermediary which may then also be responsible for the ongoing relationship with the borrower. Reference: Housing Finance, Australia (cat. no. 5609.0).
Work related condition
Long-term medical conditions reported in the survey due to an accident, incident or exposure, and which the respondent identified as work related. Reference: National Health Survey: Summary of Results (cat. no. 4364.0).
World Heritage Areas
Places that have natural and/or cultural values of outstanding universal significance, as established by the World Heritage Convention. Reference: Australia's State of the Forests Report, 2003, Bureau of Rural Sciences.
Year of occurrence
Data presented on year of occurrence basis relate to the date the event occurred. Reference: Births, Australia (cat. no. 3301.0).
Year of registration
Data presented on year of registration basis relate to the date the event was registered. Reference: Births, Australia (cat. no. 3301.0).
Youth Allowance
A government payment to full-time students aged 16-24 years and young people aged under 21 years who are undertaking job search or a combination of approved activities. Reference: Centrelink.
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All