|
|
Feature Article - WA's Merchandise trade with the rest of the world
(This article was published in the September quarter 2000 issue of Western Australian Statistical Indicators (ABS Catalogue Number 1367.5))
INTRODUCTION
Western Australia's continuing strong growth in international merchandise trade is making a significant contribution to the state's buoyant economy. While Western Australia's Gross State Product (GSP) has been growing at an average annual rate of 6% in the nine years to 1998-1999 (the latest data available), the trade surplus (Exports less Imports) has been growing at an average annual rate of 9%. The state's ability to trade successfully with the rest of the world is helping to consolidate Western Australia's position as one of Australia's leading exporting states.
PATTERN OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA'S INTERNATIONAL MERCHANDISE TRADE
Western Australia's goods exports continue to be firmly based on extensive natural resources. In 1999-2000, exports of gold bullion, iron ore, nickel, natural gas and petroleum and petroleum products accounted for 53% of the state's exports to foreign countries.
Over the last ten years, the value of exports has increased by an average of 11% annually, from $10,139 million in 1989-1990 to $25,428 million in 1999-2000. Imports also increased by an average of 11% annually over the same period, from $3,983 million to $9,518 million. The trade surplus in 1999-2000 was $15,910 million. Since the 1950's, Western Australia has enjoyed a trade surplus. This contrasts markedly with the national position, where Australia's merchandise trade has been in deficit for the last six financial years, the highest deficit over this period of $12,898 million being recorded in 1999-2000.
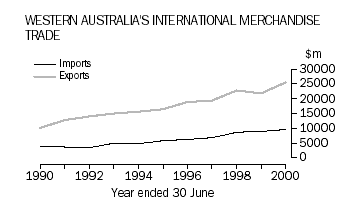
- Since 1989-1990, Western Australia has been Australia's major exporting state, accounting for a quarter of Australia's total exports. By contrast, the state's merchandise imports have averaged 8% of the value of Australia's imports over the same period; and
- In 1989-1990, Western Australia's exports comprised 27% of GSP. By 1998-1999, the proportion was 35%, down on the 37% recorded in 1997-1998. By comparison, Australia's exports were 19% of gross domestic product in 1998-1999, increasing only marginally from 16% in 1989-1990.
EXPORTS
MAJOR COMMODITIES
Western Australia's position as Australia's major exporting state is based on exports of goods classified to four of the ten main commodity groups:
- Mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials (Petroleum and petroleum products and Natural gas): comprising 24% of the value of Western Australia's exports in 1999-2000;
- Crude materials, inedible, except fuels (mainly Iron ore and Textile fibres): 21%;
- Commodities and transactions not elsewhere classified, which includes Combined confidential items (including Alumina, mineral sands and some agricultural products): 19%; and Non-monetary gold: 12%; and
- Food and live animals (mainly Wheat and Fish and crustaceans): 12%.
These groups contributed 88% of the state's export income in 1999-2000.
WESTERN AUSTRALIAN EXPORTS - SELECTED COMMODITIES, By Value of Trade
|
 | 1989-1990
| 1999-2000
|
 |  |  |  |  |
| Commodity | $m | % of total | $m | % of total |
|
| Food and live animals(a) | 1,646 | 16.2 | 2,970 | 11.7 |
Cereals and cereal preparations
| 1,010 |  | 1,642 |  |
Fish (not marine mammals), crustaceans, molluscs and aquatic
|  |  |  |  |
invertebrates, and preparations thereof
| 226 |  | 526 |  |
Live animals other than fish, crustaceans, molluscs and aquatic
|  |  |  |  |
|
| 68 |  | 299 |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Beverages and tobacco | 2 | 0.0 | 19 | 0.1 |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Crude materials, inedible, except fuels(a) | 3,412 | 33.7 | 5,430 | 21.4 |
Metalliferous ores and metal scrap
| 2,407 |  | 4,426 |  |
Textile fibres and their wastes
| 772 |  | 469 |  |
Oil seeds and oleaginous fruits
| - |  | 294 |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Mineral fuels, lubricants, and related materials(a) | 938 | 9.3 | 6,111 | 24.0 |
Petroleum, petroleum products and related materials
| 600 |  | 3,746 |  |
Gas, natural and manufactured
| 338 |  | 2,365 |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Animal and vegetable oils, fats and waxes | 13 | 0.1 | 20 | 0.1 |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Chemical and related products(a) | 272 | 2.7 | 790 | 3.1 |
Dyeing, tanning and colouring materials
| 178 |  | 407 |  |
|
| 87 |  | 209 |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Manufactured goods classified chiefly by material(a) | 127 | 1.3 | 1,509 | 5.9 |
|
| 14 |  | 1,109 |  |
Non-metallic mineral manufactures, n.e.s.
| 86 |  | 224 |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Machinery and transport equipment(a) | 146 | 1.4 | 626 | 2.5 |
Transport equipment (excl. road vehicles).
| 62 |  | 222 |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Miscellaneous manufactured articles n.e.s. | 31 | 0.3 | 77 | 0.3 |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Commodities and transactions n.e.c.(a) | 3,549 | 35.0 | 7,876 | 31.0 |
Combined confidential items
| 2,904 |  | 4,768 |  |
Gold, non-monetary (excl. gold ores and concentrates)
| 332 |  | 3,008 |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Total Exports | 10,139 | 100.0 | 25,428 | 100.0 |
|
| (a) The sum of the components may not add to totals as some commodities are not listed in the breakdown. |
| Source: ABS FASTTRACCS Service, July 2000. |
In the ten years to 1999-2000, the value of exports increased by $15,289 million. Commodity exports which increased significantly in value during this period were Petroleum and petroleum products, contributing $3,146 million of the increase in the value of exports; Non-monetary gold, contributing $2,676 million; and Natural and manufactured gas, contributing $2,026 million.
Other commodities to record significant export growth were Non-ferrous metals - from $14 million in 1989-1990 to $1,109 million in 1999-2000 (of which nickel accounted for $1,029 million); Live animal exports - from $68 million to $299 million; Oil seeds (Canola) - from an insignificant amount to $294 million; and Transport equipment (excluding road vehicles), around 95% comprising ships and boats, which increased in value from $62 million to $222 million.
Another view of Western Australian exports is provided by the ABS' Manufacturing Industry Survey. In 1997-1998 (the latest data available), Western Australian manufacturers directly exported 24% of the goods that they produced. This compares with 20% in 1994-1995 when this information was first collected. In 1997-1998, manufacturers exports were valued at $3,923 million, of which Metal product manufacturers contributed $2,039 million (or 52%).
MAJOR EXPORT MARKETS
Western Australia's top export markets (those with a value of export trade over $1,000 million) accounted for 68% of exports in 1999-2000. Japan continues to be the state's major export partner with exports in 1999-2000 worth $6,580 million (or 26% of export trade).
WESTERN AUSTRALIAN EXPORTS - MAJOR DESTINATIONS, By Value of Trade(a)(b)
|
 | 1989-1990
| 1999-2000
|
 |  |  |  |  |
 | $m | % of total | $m | % of total |
|
 | COUNTRIES |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Japan | 2,751 | 27.1 | 6,580 | 25.9 |
| Republic of Korea | 478 | 4.7 | 2,318 | 9.1 |
| United States of America | 1,699 | 16.8 | 2,287 | 9.0 |
| Singapore | 473 | 4.7 | 1,905 | 7.5 |
| China | 501 | 4.9 | 1,867 | 7.3 |
| Taiwan | 280 | 2.8 | 1,351 | 5.3 |
| United Kingdom | 232 | 2.3 | 1,065 | 4.2 |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Total Exports | 10,139 | 100.0 | 25,428 | 100.0 |
|
 | COUNTRY GROUPS(c) |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Asia Pacific Economic Co-operation (APEC) | 7,045 | 69.5 | 19,042 | 74.9 |
| Developing Countries | 3,560 | 35.1 | 11,413 | 44.9 |
| European Union | 1,385 | 13.7 | 3,502 | 13.8 |
| Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) | 983 | 9.7 | 3,414 | 13.4 |
|
| (a) The sum of the components do not add to totals as all countries are not listed in the breakdown. |
| (b) Excludes data subject to confidentiality restrictions. |  |  |  |  |
| (c) A country may belong to more than one country group e.g China is included in APEC and Developing Countries. |
| A list of component countries is published in International Merchandise Trade, Australia (cat.no.5422.0). |
| Source: ABS FASTTRACCS Service, July 2000. |  |  |  |  |
Since 1989-1990, the United States of America moved from being the state's second largest export destination in dollar terms (with 17% of exports) to our third largest destination in 1999-2000 (with 9% of exports). While exports to the United States have increased by a significant $588 million over that ten year period, there has been a stronger rate of growth in exports to South East Asian and North Asian countries. The Republic of Korea led the way, with exports to that country increasing five times to be worth $2,318 million in 1999-2000 making it Western Australia's second largest export destination. Korea, together with Singapore (which increased four times to $1,905 million), China (increasing almost four times to $1,867 million) and Taiwan (increasing almost five times to $1,351 million) accounted for 29% of the state's export market in 1999-2000, up from 17% of the market ten years ago.
Of the selected country groups with which Western Australia trades, exports to ASEAN (up an average annual increase of 16%) and to Developing Countries (up an average annual increase of 13%) recorded the greatest increases in the ten years to 1999-2000. For our ASEAN neighbours, Singapore continues to dominate exports (56% of total state exports to ASEAN in 1999-2000) while strong growth was recorded for Thailand (from $30 million in 1989-1990 to $333 million in 1999-2000), the Philippines (from $48 million to $201 million) and Viet Nam ($516 thousand to $57 million).
SELECTED EXPORT COMMODITIES AND THEIR DESTINATIONS
A significant proportion of Western Australia's commodity exports are, for data confidentiality reasons, unable to be published according to their country of destination. Commodities subject to restrictions include Natural gas, Wheat, Nickel and Alumina.
The more significant commodities exported in 1999-2000, not subject to confidentiality restrictions, were:
- Iron ore and concentrates (15% of state exports). Japan dominated the market, accounting for 46% of total Iron ore exports. China ranked second, receiving just under a quarter (23%) of exports. Iron ore exports to China in 1999-2000 represented 46% of the state's exports to that country;
- Petroleum and petroleum products (15% of state exports). The Republic of Korea has risen steadily to become the state's top Petroleum export destination in 1999-2000 ($756 million), just ahead of the United States of America ($734 million); and
- Non-monetary gold (12% of state exports). Singapore received 38% of Western Australia's Non-monetary gold exports in 1999-2000. At $1,150 million, this represents 60% of the state's exports to Singapore.
WESTERN AUSTRALIAN EXPORTS: SELECTED MAJOR COMMODITIES AND MAJOR DESTINATIONS, By Value of Trade(a)(b), 1999-2000
|
 |  |  |  |  |
| Commodity and destination | $m |  | Commodity and destination | $m |
|
| Iron ore and concentrates | 3,769 |  | Natural gas | 1,949 |
| Japan | 1,730 |  |
|  |
| China | 850 |  |  |  |
| Republic of Korea | 495 |  | Wheat (incl. spelt) and meslin, unmilled | 1,568 |
| Taiwan | 263 |  |
|  |
| United Kingdom | 115 |  |  |  |
| France | 100 |  | Nickel | 1,029 |
 |  |  |
|  |
| Petroleum and petroleum products | 3,746 |  |  |  |
| Republic of Korea | 756 |  | Fish and crustaceans | 526 |
| United States of America | 734 |  |
| 194 |
| Japan | 678 |  |
| 132 |
| Taiwan | 502 |  |
| 84 |
| Singapore | 484 |  |
| 70 |
| New Zealand | 260 |  |
| 17 |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Non-monetary gold | 3,008 |  | Wool | 468 |
| Singapore | 1,150 |  |
| 161 |
| United Kingdom | 501 | |
| 80 |
| Republic of Korea | 429 | |
| 58 |
| Japan | 283 | |
| 42 |
| Thailand | 137 |  |
| 33 |
| Switzerland | 107 |  |  |  |
|
| (a) The sum of the components may not add to the totals as some countries are not listed in the commodity breakdown. |
| (b) Excludes data subject to confidentiality restrictions. |
| Source: ABS FASTTRACCS Service, July 2000. |
Japan and China are also important markets for a number of other commodity exports. In 1999-2000, Japan received $320 million of Liquified Petroleum Gas, and $194 million (or 37%) of Fish and crustaceans exports. China accounted for $161 million (34%) of the state's wool exports and $160 million (54%) of the growing Canola exports.
IMPORTS
While strong world demand for Western Australia's rich resources has positioned the state as Australia's leading exporter, demand for merchandise imports is driven more by the need to sustain the state's industry and population. As such, Western Australia ranked fourth (after the larger eastern states) in terms of its contribution to the value of Australia's imports (9% in 1999-2000).
MAJOR COMMODITIES
Of all Western Australian imports, 70% of the total value in 1999-2000 related to three commodity groups:
- Machinery and transport equipment: accounting for 38% of Western Australia's imports. In the main, this group comprised Road vehicles ($1,053 million); Machinery specialised for particular industries ($661 million); and Office machines and computing equipment ($613 million);
- Non-monetary gold: 19% of the state's imports;and
- Mineral fuels, lubricants, and related materials: 13% of the state's imports and comprised almost entirely of imports of Petroleum, petroleum products and related materials worth $1,282 million.
WESTERN AUSTRALIAN IMPORTS: SELECTED COMMODITIES, By Value of Trade
|
 | 1989-1990
| 1999-2000
|
 |  |  |  |  |
| Commodity | $m | % of total | $m | % of total |
|
| Food and live animals | 98 | 2.5 | 184 | 1.9 |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Beverages and tobacco | 16 | 0.4 | 29 | 0.3 |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Crude materials, inedible, except fuels | 110 | 2.8 | 81 | 0.8 |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Mineral fuels, lubricants, and related materials(a) | 670 | 16.8 | 1,282 | 13.5 |
| Petroleum, petroleum products and related materials | 669 |  | 1,282 |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Animal and vegetable oils, fats and waxes | 10 | 0.2 | 16 | 0.2 |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Chemicals and related products(a) | 294 | 7.4 | 795 | 8.4 |
|
| 46 |  | 288 |  |
Fertilisers (excl. crude)
| 72 |  | 214 |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Manufactured goods classified chiefly by material | 592 | 14.9 | 1,016 | 10.7 |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Machinery and transport equipment(a) | 1,671 | 41.9 | 3,635 | 38.2 |
Road vehicles (incl. air-cushion vehicles)
| 399 |  | 1,053 |  |
Machinery specialised for particular industries
| 371 |  | 661 |  |
Office machines and computing equipment
| 51 |  | 613 |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Miscellaneous manufactured articles | 267 | 6.7 | 488 | 5.1 |
| Commodities and transactions n.e.c.(a) | 255 | 6.4 | 1,992 | 20.9 |
Gold, non-monetary (excl. gold ores and concentrates)
| 1 |  | 1,781 |  |
Combined confidential items
| 219 |  | 199 |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Total Imports | 3,983 | 100.0 | 9,518 | 100.0 |
|
| (a) The sum of the components may not add to totals as some commodities are not listed in the breakdown. |
| Source: ABS FASTTRACCS Service, July 2000. |  |  |  |  |
Non-monetary gold imports have been the major growth commodity, increasing substantially from negligible value ten years ago to be worth $1,781 million in 1999-2000. The next highest valued import was Petroleum, petroleum products and related materials which contributed 13% of total imports.
Other imported commodities to have increased significantly in value over the last ten years have been Office machines and computing equipment, increasing twelve times to $613 million in 1999-2000 and Organic chemicals, increasing over six times to $288 million.
MAJOR IMPORT MARKETS
The United States of America and Japan have traditionally vied as Western Australia's major source of imports. In 1999-2000, the United States of America was the state's main supplier with 17% ($1,587 million) of imports followed by Japan with 10% ($985 million).The Republic of Korea was the state's third largest source of imported commodities, having increased markedly from supplying 2% of state imports ten years ago to 9% in 1999-2000.
WESTERN AUSTRALIAN IMPORTS: MAJOR SOURCES, By Value of Trade(a)(b)
|
 | 1989-1990
| 1999-2000
|
 |  |  |  |  |
 | $m | % of total | $m | % of total |
|
 | COUNTRIES |
 |  |  |  |  |
| United States of America | 639 | 16.0 | 1,587 | 16.7 |
| Japan | 798 | 20.0 | 985 | 10.3 |
| Republic of Korea | 68 | 1.7 | 858 | 9.0 |
| Singapore | 145 | 3.6 | 628 | 6.6 |
| Indonesia | 131 | 3.3 | 496 | 5.2 |
| United Kingdom | 259 | 6.5 | 470 | 4.9 |
| Viet Nam | 2 | 0.1 | 424 | 4.4 |
| Total Imports | 3,983 | 100.0 | 9,518 | 100.0 |
|
 | COUNTRY GROUPS(c) |
 |  |  |  |  |
| Asia Pacific Economic Co-operation (APEC) | 2,307 | 57.9 | 6,779 | 71.2 |
| Developing Countries | 1,288 | 32.3 | 4,165 | 43.8 |
| Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) | 375 | 9.4 | 2,039 | 21.4 |
| European Union | 891 | 22.4 | 1,681 | 17.7 |
|
| (a) The sum of the components do not add to totals as all countries are not listed in the breakdown. |
| (b) Excludes data subject to confidentiality restrictions. |
(c) A country may belong to more than one country group e.g. Republic of Korea is included in APEC and Developing Countries.
A list of component countries is published in International Merchandise Trade, Australia (cat.no.5422.0). |
| Source: ABS FASTTRACCS Service, July 2000. |  |  |  |  |
The majority of Western Australia's goods imports are sourced from APEC and European Union countries. Countries comprising our nearest neighbour ASEAN have, in the main, significantly increased their contribution to state imports, particularly Viet Nam, Thailand, Malaysia and Singapore. As a result, the value of goods imported from ASEAN in 1999-2000 accounted for 21% of the state's import trade compared with 9% ten years ago.
SELECTED IMPORT COMMODITIES AND THEIR COUNTRY OF ORIGIN
The Republic of Korea and Viet Nam were the main contributors to Western Australia's top commodity imports (Non-monetary gold and Crude petroleum) in 1999-2000:
- Non-monetary gold (19% of state imports). The Republic of Korea provided 35% of Non-monetary gold imports. Of total imports sourced from Korea, Non-monetary gold accounted for 73%; and
- Crude petroleum (11% of state imports). Viet Nam has risen markedly over the last ten years to become the state's main supplier (40%) of this commodity.
WESTERN AUSTRALIAN IMPORTS: SELECTED MAJOR COMMODITIES AND MAJOR COUNTRIES OF ORIGIN, By Value of Trade(a)(b), 1999-2000
Japan's dominance as a supplier of motor vehicle imports continued in 1999-2000, with 62% of Private motor vehicles and 39% of Motor vehicles for transporting goods (including off-road vehicles). Singapore was the leading supplier (38%) of the high growth import commodity Automatic data processing machines (mainly computers).
REFERENCES
ABS FASTTRACCS Service. An ABS special data service providing customised international merchandise trade statistics.
International Merchandise Trade, Australia (cat.no.5422.0).
Australian National Accounts: Quarterly State Details (cat.no.5204.0.40.001)- an ABS special data service.
Australian System of National Accounts (cat.no.5204.0).
Manufacturing Industry, WA (cat.no.8221.5).
PRINTER FRIENDLY VERSION OF "WA'S MERCHANDISE TRADE WITH THE REST OF THE WORLD"
| 
(188Kb) |
|
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All