EARLY CHILDHOOD EDUCATION
Early childhood education in Australia encompasses early learning programs in preschools and other organisations, and the skills development of children from birth onwards. A number of studies at the domestic and international level have noted that young children who do not have appropriate learning opportunities may suffer from adverse outcomes later in life, although difficulties may be overcome by quality interventions which support families and individuals. Research also indicates that children are at the peak of their learning potential up to the age of 8 years. This has prompted educational providers to introduce formal programs to maximise the uptake of basic skills in the early years. Such programs, aimed at raising children's readiness for school, are generally available in preschool and a range of child-care settings.
Preschool students
Preschool generally refers to education that is provided for children from age 3 years to school starting age. The responsibility for providing preschool education rests with individual states and territories. Preschools may be operated by government, community organisations or the private sector. They are largely sessional and normally only operational during school terms. Preschool programs may also be provided in long-day child care centres.
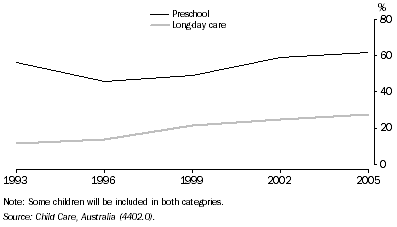
The age at which children may attend preschool varies across jurisdictions, reflecting the different school commencement ages. In June 2005, according to the triennial Child Care Survey, conducted by the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS), 62% of 4 year olds attended preschool (graph 12.1). At that time, 62% of all preschoolers were aged 4 years.
12.1 Participation of four year olds - June
The National Preschool Census (NPC), conducted annually for the Australian Government Department of Education, Science and Training collects information about all 3-5 year olds attending preschools which are registered providers and have a preschool educational program. The NPC found 4,898 in-scope preschools, with 213,000 children enrolled at August 2006, a fall of 4% from the previous year's enrolments. Government preschools held 76% of enrolled children.
Indigenous preschool students
The NPC provides a basis for the allocation of Australian Government funding to preschools in which Indigenous students are enrolled. The 2006 NPC reported 9,275 Indigenous children enrolled in government and non-government preschools, representing 4% of total preschool enrolments. Of these enrolments, 30% were in New South Wales. Between 2005 and 2006, the number of Indigenous children enrolled in preschools increased by 3%, while non-Indigenous enrolments decreased by 4% (table 12.2). Indigenous enrolments were reported by 1,765 preschools.
12.2 INDIGENOUS PRESCHOOL ENROLMENTS |
|  |
 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 |  |
|  |
| New South Wales | 2 694 | 2 672 | 2 773 | 2 763 |  |
| Victoria | 559 | 535 | 523 | 597 |  |
| Queensland(a) | 896 | 862 | 738 | 810 |  |
| South Australia | 1 114 | 1 148 | 1 047 | 1 066 |  |
| Western Australia | 1 834 | 1 858 | 1 905 | 2 127 |  |
| Tasmania | 331 | 341 | 356 | 322 |  |
| Northern Territory | 1 535 | 1 544 | 1 543 | 1 477 |  |
| Australian Capital Territory | 88 | 95 | 134 | 113 |  |
| Total Indigenous enrolments | 9 051 | 9 055 | 9 019 | 9 275 |  |
| Total non-Indigenous enrolments | 211 627 | 205 004 | 212 653 | 203 723 |  |
|  |
| (a) Some Queensland enrolments are excluded from the National Preschool Census. Consequently, Indigenous preschool enrolments are understated. |
| Source: Department of Education, Science and Training, 'National Preschool Census'. |
 Print Page
Print Page