| ENERGY SURVEY, 2007-08
Please note that this datacube is associated with the publication 8155.0 Australian Industry, 2007-08. The estimates presented here have been compiled using data, from survey questionnaires and other ABS sources, which are additional to the data used in compiling the estimates in that publication, and using different methodology. This methodology has allowed estimates of electricity and gas production, transmission and distribution to be presented together with detailed financial estimates for the associated industries.
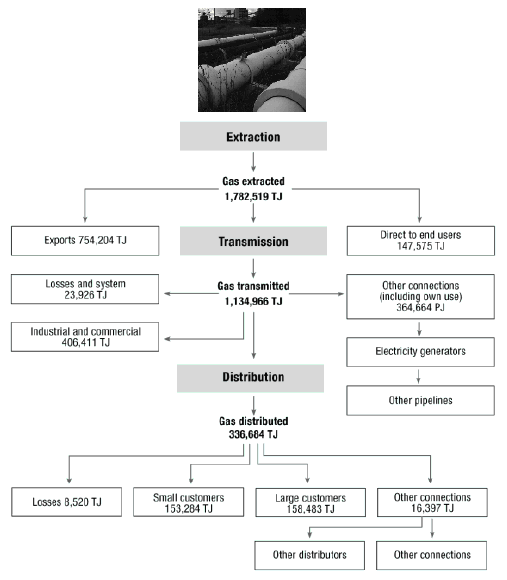
GAS SUPPLY CHAIN
The following diagram shows the gas supply chain and the relationship between the data items presented.
The data excludes any gas extracted outside of Australian territory. The data is presented based on the industry classification of the reporting businesses. An alternative view based on activity is presented in ABS publication 4647.0 Alternative View of Electricity and Gas Supply Activity.
The natural gas supply chain begins with extracting gas from wells. The extracted gas is processed to separate the methane from the liquids and other gases that may be present, and to remove any impurities. More commonly gas fields and processing facilities are located some distance from the cities, towns and regional centres where the gas is consumed. High pressure transmission pipelines are used to transport natural gas from the source of extraction over long distances from production fields to major demand centres. Distribution pipelines deliver gas from points along the transmission pipelines to industrial customers, and from gate stations to consumers in cities, towns and regional communities.
GLOSSARY
For definitions of other data items, not specific to the Energy Survey, please see the main Glossary from the Explanatory Notes tab.
Distribution: Distribution pipelines deliver gas from points along the transmission pipelines to industrial customers, and from gate stations (or city gates) to consumers in cities, towns and regional communities. A distribution network typically consists of high, medium and low pressure pipelines. The high and medium pressure pipelines are used to service areas of high demand and to provide the ‘backbone’ of the network (for example, transporting gas between population concentrations within a distribution area). The low pressure pipes lead off the higher pressure mains to the end customer.
Domestic Industrial/Commercial: Customers who use gas in their business or industrial activities.
End user: Defined as a customer who is supplied electricity directly from the gas producer/extractor.
Extraction: The natural gas supply chain begins with exploration and development activity, which may involve geological surveys and the drilling of wells. Exploration typically occurs in conjunction with the search for other hydrocarbon deposits, such as oil. At the commercialisation phase, the extracted gas is processed to separate the methane from the liquids and other gases that may be present, and to remove any impurities, such as water and hydrogen sulphide. Gas is extracted from wells and may be used on-site as a fuel for electricity generation or for other purposes. More commonly, however, gas fields and processing facilities are located some distance from the cities, towns and regional centres where the gas is consumed.
Large customer connections: Customers to whom distribution business distributed 10 terajoules or more per annum and/or (Victoria excluded) would not qualify for a regulated or codified tariff.
Pipeline Transport: High pressure transmission pipelines are used to transport natural gas from the source of extraction over long distances from production fields to major demand centres. The pipelines typically have wide diameters and operate under high pressure.
Small customer connections: Customers to whom distribution business distributed less than 10 terajoules to per annum and/or (Victoria excluded) which qualify for a regulated or codified tariff.
Terajoule: Unit of measurement of processed natural gas equal to one million million (1012) joules, Abbreviated as TJ.
METHODOLOGY
The Energy Survey was conducted as a census (by ANZSIC and activity) of all businesses involved with gas supply. |