|
|
Contents >>
Appendix 3: International Classification of Diseases
Introduction
The World Health Organization (WHO) International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is used to code illness and death to produce Australia's morbidity and mortality statistics. This appendix provides a guide to the ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes which are of interest to researchers and analysts interested in illnesses and deaths attributed directly to the use of illicit drugs. Tables of relevant ICD codes are provided to illustrate the lack of specificity which restricts the information pertaining to individual illicit drugs.
Example of available data
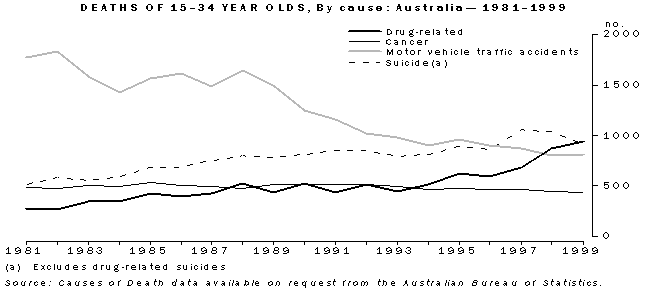
Morbidity
The modified versions of ICD used by hospitals for morbidity coding are known as ICD-9-CM (9th Revision, Clinical Modification) and ICD-10-AM (10th Revision, Australian Modification). The structure of these classifications is very similar to that used for mortality coding, but is not necessarily directly comparable. The broad issues identified below for mortality coding will generally apply to morbidity coding as well.
Mortality
All deaths registered from 1979 to 1998 have been coded by the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) to ICD-9, with previous editions being used for deaths prior to 1979. Deaths registered from 1 January 1997 have been coded using the tenth revision, ICD-10. Deaths registered in 1997 and 1998 were dual coded in both ICD-9 and ICD-10 to enable the production of comparability factors between the two series.
For drug-related deaths, the ICD does not focus on the identity of the drug(s) involved, but rather on the circumstance of the death. For example, deaths that were determined to be directly caused by drug use could be classified as being due to external causes (e.g. assault, accident, or suicide) or due to mental or behavioural disorders associated with drug use. As a result of this different focus, the codes assigned may not be unique to any specific drug. For example, in ICD-9, all deaths for which the underlying cause was psychosis due to drug use (whether opioids, amphetamines, barbiturates or other drugs) were coded to 292.
The following tables illustrate the lack of specificity in the ICD codes. In particular, they illustrate the extent to which specific ICD codes can be used to identify individual drugs. This will vary depending on the nature of the death. The tables do not include all the codes, either in ICD-9 or ICD-10, required to identify all drug-related deaths (e.g. in the graph above). Rather they highlight the types of drugs which are relevant to this publication.
Researchers and analysts wishing to obtain data on drug-related deaths from the Causes of Death collection or the National Mortality Database may be guided by the tables. However, to identify the full set of codes most relevant to their requirements, researchers should consult the ICD manuals and/or the experts at ABS or AIHW.
Guide to ICD codes applicable to deaths from illicit drugs
Table A3.1 presents the ICD-9 codes used to classify deaths in Australia which are directly caused by selected groups of drugs including illicit drugs. If evidence of more than one drug was found in the body, the combination codes would be used rather than the more specific codes.
Table A3.2 presents the equivalent codes for ICD-10. Further detail is provided on mental and behavioural disorders by a fourth character which indicates the type of substance use, such as dependence, harmful use, psychosis or withdrawal for those deaths.
The table also presents a list of poison codes which are used to provide further detail on the drug-related deaths coded to an external cause. If more than one drug is found in the body, more than one poison code is assigned. Although ICD-10 does not have a unique poison code for all drugs, many drugs of interest can be identified by cross-tabulating the data using the appropriate external cause code and the poison code. For example, if a coroner determined a death to be an accidental heroin overdose, the death would be assigned ICD codes: X42 (accidental poisoning) and T40.1 (poisoning by heroin). In ICD-10, codes for external causes are presented in Chapter XX while poison codes are in Chapter XIX.
Table A3.3 provides a code descriptor for each of the ICD-10 codes mentioned in Table A3.2, to clarify the classification. Further details of the ICD-10 codes are available from the three volumes of the publication International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision, published in 1992, 1993 and 1994 by WHO.
A3.1 CD-9 CODES FOR DEATHS CAUSED BY SELECTED DRUGS
 |  | Mental and behavioural disorders
|
| | |  |  |  |
| Drug type | Example/common name | Dependence | Non-dependent abuse | Psychoses |
| Multiple drug use | - | 3047, 3048 | 3059 | 292 |
| Cannabis | Grass, Hashish, Pot | 3043 | 3052 | 292 |
| Cocaine | Coke, Crack, White lady | 3042 | 3056 | 292 |
| Hallucinogens | LSD, Mescaline, Psilocybin | 3045 | 3053 | 292 |
| Opioids | Heroin, Morphine, Codeine | 3040, 3047 | 3055 | 292 |
| Psychostimulants | Amphetamine, Ecstasy | 3044 | 3057 | 292 |
| Barbiturates | Barbs, Phenobarbitone | 3041 | 3054 | 292 |
| Tranquillisers/sedatives | Benzodiazepine, Valium, Serepax | 3041 | 3054 | 292 |
|
A3.1 CD-9 CODES FOR DEATHS CAUSED BY SELECTED DRUGS continued
| | | External causes (poisoning)
|
| Drug type | Example/common name | Assault | Accident | Suicide | Undetermined intent |
| Multiple drug use | - | E9620 | E8588 (a) | E9504 (a) | E9804 (a) |
| Cannabis | Grass, Hashish, Pot | E9620 | E8541 | E9503 | E9803 |
| Cocaine | Coke, Crack, White lady | E9620 | E8552 (b) | E9504 (c) | E9804 (c) |
| Hallucinogens | LSD, Mescaline, Psilocybin | E9620 | E8541 | E9503 | E9803 |
| Opioids | Heroin, Morphine, Codeine | E9620 | E8500 | E9500 (d) | E9800 (d) |
| Psychostimulants | Amphetamine, Ecstasy | E9620 | E8542 | E9503 | E9803 |
| Barbiturates | Barbs, Phenobarbitone | E9620 | E8519 | E9501 | E9801 |
| Tranquillisers/sedatives | Benzodiazepine, Valium, Serepax | E9620 | E852, E853 | E9502, E9503 | E9802, E9803 |
(a) From 1997, deaths from multiple drug use were coded to E8588 (accident), E9504 (suicide), or E9804 (undetermined). Prior to this, only the first mentioned drug on the medical certificate was coded.
(b) Included with local anaesthetics.
(c) Included with other specified drugs and medicaments.
(d) Included with analgesics, antipyretics and antirheumatics. |
A3.2 ICD-10 CODES FOR DEATHS CAUSED BY SELECTED DRUGS
 |  |  | External causes (poisoning)
|  |
| Drug type | Example/common name | Mental and behavioural disorders(a) | Assault | Accident | Suicide | Undetermined
intent | Poison codes |
| Multiple drug use(b) | - | F19 | X85 | X44 | X64 | Y14 | - |
| Cannabis | Grass, Hashish, Pot | F12, F19 | X85 | X42, X44 | X62, X64 | Y12, Y14 | T40.7 |
| Cocaine | Coke, Crack, White lady | F14, F19 | X85 | X42, X44 | X62, X64 | Y12, Y14 | T40.5 |
| Hallucinogens | LSD, Mescaline, Psilocybin | F16, F19 | X85 | X42, X44 | X62, X64 | Y12, Y14 | T40.8, T40.9 |
| Opioids | Heroin, Morphine, Codeine | F11, F19 | X85 | X42, X44 | X62, X64 | Y12, Y14 | T40.0-T40.4, T40.6 |
| Psychostimulants | Amphetamine, Ecstasy | F15, F19 | X85 | X41, X44 | X61, X64 | Y11, Y14 | T43.6, T43.8, T43.9 |
| Barbiturates | Barbs, Phenobarbitone | F13, F19 | X85 | X41, X44 | X61, X64 | Y11, Y14 | T42.3 |
| Tranquillisers/sedatives | Benzodiazepines, Valium, Serepax | F13, F19 | X85 | X41, X44 | X61, X64 | Y11, Y14 | T42.4, T42.6, T42.7,
T43.3, T43.5 |
(a) A fourth character will give the type of substance use e.g. dependence, harmful use, psychoses.
(b) Includes deaths from multiple drug use involving a combination of drugs from different categories e.g. opiate and tranquilliser. |
A3.3 ICD-10 CODE DESCRIPTORS
|
| Cause of death | ICD-10 code |
MEDICAL CONDITIONS
|
| Mental and behavioural disorders due to use of | |
| Opioids | F11 |
| Cannabinoids | F12 |
| Sedatives or hypnotics | F13 |
| Cocaine | F14 |
| Other stimulants including caffeine(a) | F15 |
| Hallucinogens | F16 |
| Multiple drug use and use of other psychoactive substances | F19 |
| |
EXTERNAL CAUSES |
| Accidental poisoning by and exposure to | |
| Antiepileptic, sedative-hypnotic, antiparkinsonism and psychotropic drugs n.e.c. | X41 |
| Narcotics and psychodysleptics (hallucinogens) n.e.c. | X42 |
| Other and unspecified drugs, medicaments and biological substances | X44 |
Intentional self-poisoning by and exposure to | |
| Antiepileptic, sedative-hypnotic, antiparkinsonism and psychotropic drugs n.e.c. | X61 |
| Narcotics and psychodysleptics (hallucinogens) n.e.c. | X62 |
| Other and unspecified drugs, medicaments and biological substances | X64 |
Assault by drugs, medicaments and biological substances | X85 |
Event of undetermined intent by poisoning and exposure to | |
| Antiepileptic, sedative-hypnotic, antiparkinsonism and psychotropic drugs n.e.c. | Y11 |
| Narcotics and psychodysleptics (hallucinogens) n.e.c. | Y12 |
| Other and unspecified drugs, medicaments and biological substances | Y14 |
| |
POISONS |
| Poisoning by narcotics and psychodysleptics (hallucinogens) | |
| Opium | T40.0 |
| Heroin | T40.1 |
| Other opioids | T40.2 |
| Methadone | T40.3 |
| Other synthetic narcotics | T40.4 |
| Cocaine | T40.5 |
| Other and unspecified narcotics | T40.6 |
| Cannabis (derivatives) | T40.7 |
| Lysergide (LSD) | T40.8 |
| Other and unspecified psychodysleptics (hallucinogens) | T40.9 |
Poisoning by antiepileptic, sedative-hypnotic and antiparkinsonism drugs | |
| Barbiturates | T42.3 |
| Benzodiazepines | T42.4 |
| Other antiepileptic and sedative-hypnotic drugs | T42.6 |
| Antiepileptic and sedative-hypnotic drugs, unspecified | T42.7 |
Poisoning by psychotropic drugs, n.e.c. | |
| Phenothiazine antipsychotics and neuroleptics | T43.3 |
| Other and unspecified antipsychotics and neuroleptics | T43.5 |
| Psychostimulants with abuse potential (a) | T43.6 |
| Other psychotropic drugs, n.e.c. | T43.8 |
| Psychotropic drug, unspecified | T43.9 |
(a) Includes amphetamines and ecstasy. |
|
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All