SUMMARY OF FINDINGS
OVERVIEW
In June 2006 there were 175,100 children aged 5 to 14 years who worked at some time during the last 12 months (for example by delivering leaflets for an employer or cleaning or gardening for non-household members for payment). This represented 6.6% of all children aged 5 to 14 years. There were 101,000 boys who had worked (7.4% of all boys) and 74,100 girls (5.7% of all girls). The proportion of children aged 5 to 9 years who had worked was 1.8% and the proportion of children aged 10 to 14 years who had worked was 11%.
Northern Territory and Western Australia had the highest proportions of children who worked during the last 12 months (12% and 9.5% respectively). New South Wales and Victoria had the lowest proportions of children who worked during the last 12 months (each 5.8%). Across Australia, children in state capital cities were less likely to have worked in the last 12 months (5.3%) than children in the balance of state or in a territory (8.4%).
CHILDREN WHO WORKED
Of the 175,100 children who had worked at some time during the last 12 months, 54% had worked for an employer, 33% had worked in a family business or farm and 16% had worked for themselves (children may have worked in more than one type of job). These proportions were similar for boys and girls, and for children aged 10 to 14 years. However, for children aged 5 to 9 years, 56% had worked in a family business or farm and 31% had worked for an employer.
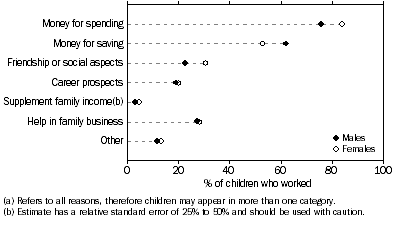
The most common reason that children worked was 'Money for spending'. For 79% of children who had worked in the last 12 months this was one of the reasons they worked, and for 51% of children it was the main reason they worked. This was followed by 'Money for saving' which for 58% of children was one of the reasons and for 24% it was the main reason they worked.
All reasons child worked in the last 12 months(a), Males and females
Over a quarter (28%) of children who worked during the last 12 months worked between 1 and 3 weeks of the year and 30% worked between 4 and 12 weeks of the year. The remaining 42% worked 13 weeks or more during the year.
WORK AND SCHOOL BALANCE
Of all children aged 5 to 14 years who worked in the last 12 months, 146,000 (83%) worked during school terms, 121,400 (69%) worked during school holidays and 92,300 (53%) worked during both school holidays and school terms.
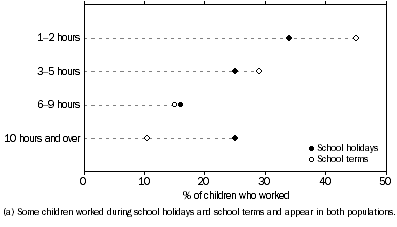
Of the children aged 5 to 14 years who worked during school terms, 45% usually worked 1 to 2 hours, 29% usually worked 3 to 5 hours and 11% usually worked 10 hours and over per week in all jobs during school terms. Of the children aged 5 to 14 years who worked during school holidays, 34% usually worked 1 to 2 hours, 25% usually worked 3 to 5 hours and 25% usually worked 10 hours and over per week in all jobs during school holidays.
Usual hours worked per week in all jobs, School holidays and school terms(a)
Of children who worked during school terms, 67% usually worked Saturday to Sunday and 58% usually worked Monday to Friday during school terms. The most common times of the day usually worked were between 3pm and 5pm on Mondays to Fridays and between 9am and 12pm on Saturdays and Sundays (40% and 34% of children who worked during school terms respectively).
Of children who worked during school holidays, 63% usually worked Saturday to Sunday and 73% usually worked Monday to Friday during school holidays. The most common times of the day usually worked during school holidays were between 9am and 12pm and between 3pm and 5pm (50% and 48% of children who worked during school holidays respectively).
OCCUPATION OF MAIN JOB
The most common occupation for boys in their main job during school terms was 'Leaflet or Newspaper Deliverer' (24%), while 'Farm, Forestry and Garden Workers' was the most common occupation for boys in their main job during school holidays (26%). For girls, the most common occupation in their main job during both school holidays and school terms was 'Sales Workers' (17% and 20% respectively).
TRAVEL TO WORK
The most common way for children to travel to and from work was by 'Private motor vehicle with parents' (45% of boys and 57% of girls), followed by walking (25% of boys and 21% of girls). About one in five children (18% of boys and 21% of girls) worked from home or did not need to travel to and from work.
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All