SEPTEMBER KEY FIGURES
 |  | September 2013 | August 2013 to September 2013 |
 |  | $m | % change |
|
| Turnover at current prices |  |  |
 | Trend | 22 040.6 | 0.3 |
 | Seasonally Adjusted | 22 145.5 | 0.8 |
|
 |  | September Qtr 2013 | June Qtr 2013 to September Qtr 2013 |
 |  | $m | % change |
|
| Turnover in volume terms |  |  |
 | Trend | 65 538.1 | 0.6 |
 | Seasonally Adjusted | 65 473.5 | 0.7 |
|
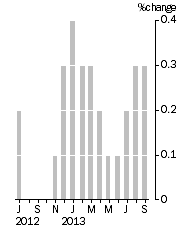
Monthly Turnover, Current Prices - Trend Estimate
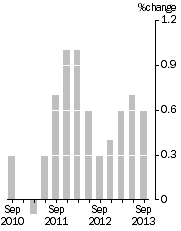
| Quarterly Turnover, in volume terms - Trend estimate
|
SEPTEMBER KEY POINTS
CURRENT PRICES
- The trend estimate rose 0.3% in September 2013. This follows a rise of 0.3% in August 2013 and a rise of 0.2% in July 2013.
- The seasonally adjusted estimate rose 0.8% in September 2013. This follows a rise of 0.5% in August 2013 and a rise of 0.1% in July 2013.
- In trend terms, Australian turnover rose 2.6% in September 2013 compared with September 2012.
- The following industries rose in trend terms in September 2013: Clothing, footwear and personal accessory retailing (1.3%), Food retailing (0.2%), Household goods retailing (0.4%), Cafes, restaurants and takeaway food services (0.4%), Other retailing (0.1%) and Department stores (0.2%).
- The following states and territories rose in trend terms in September 2013: Victoria (0.5%), New South Wales (0.2%), Queensland (0.3%), South Australia (0.6%), Tasmania (0.7%), the Northern Territory (1.0%) and the Australian Capital Territory (0.1%). Western Australia (0.0%) was relatively unchanged in trend terms in September 2013.
VOLUME MEASURES
- In volume terms, the trend estimate for Australian turnover rose 0.6% in the September quarter 2013.
NOTES
FORTHCOMING ISSUES
| ISSUE | Release Date |
| October 2013 | 3 December 2013 |
| November 2013 | 9 January 2014 |
| December 2013 | 6 February 2014 |
| January 2014 | 6 March 2014 |
| February 2014 | 3 April 2014 |
| March 2014 | 7 May 2014 |
CHANGES IN THIS ISSUE
- This issue includes a feature article on the coverage of Household Final Consumption Expenditure (HFCE) provided by this publication. A new appendix is also included with experimental estimates of consumer sales of electricity and gas, with the aim of improving the coverage of HFCE provided by this publication.
- The reference and base year for chain volume estimates is updated each September. A new base year, 2011-12, has been introduced into the chain volume estimates which has resulted in revisions to growth rates in subsequent periods. The chain volume estimates have also been re-referenced to 2011-12. Additivity is preserved in the quarters of the reference year and subsequent quarters. Re-referencing affects the level of, but not the movements in, chain volume estimates.
- This September, the chain volume estimates have also been revised as result of changes to the price deflator weights and the mapping of weights to detailed price indexes. These changes aim to improve the coherence between the price deflators used for Retail Trade and the price deflators used for HFCE in the Australian System of National Accounts. These changes have resulted in revisions to the chain volume estimates from the September quarter 2009 through to the June quarter 2013.
CHANGES IN NEXT ISSUE
The next issue (October 2013) will introduce changes to the sample design and methodology of the Retail Business Survey. The annualised turnover benchmarks used for stratification purposes will be updated from a static version of the Business Activity Statement (BAS) turnover (which was last updated in the September quarter 2009) to the most recent value of the BAS turnover which will be updated quarterly. This new methodology will improve the accuracy of estimates derived from the survey and address the issue of ageing stratification benchmarks which must be periodically updated.
Estimates of movement in the implementation month will be subject to higher volatility than usual. In addition, lower level time series may be impacted by a random shift in level. In subsequent issues, the ABS will assess the size of any level shifts and consider revisions to historical series to facilitate comparisons over time. The impact of changes on levels may be estimated from the first two cycles which use the new methodology and any potential revisions to smooth level shifts into monthly and quarterly series would be applied for the next quarterly issue (December 2013).
INQUIRIES
For further information about these and related statistics, contact the National Information and Referral Service on 1300 135 070 or Paul Slater on Sydney (02) 9268 4581.
 Print Page
Print Page
 Print All
Print All